Step into a world of academic excellence with Rapid Assignment Help’s unparalleled Assignment Help services.
The dynamic domain of the construction industry, the position of the construction manager holds significant importance, having an important impact on the basic elements of prosperous undertakings. This paper examines the various aspects of a construction manager's duties, including their positions, complex tasks, and approaches to management, behavioural characteristics, ethical considerations, and steadfast dedication to safety and wellness at work. Construction managers assume multiple roles as the administrators of construction projects. Architects not only possess the ability to transform architectural concepts into tangible structures, but they also adeptly manage the intricate aspects of financial constraints, project schedules, and available resources. The proficient utilization of sophisticated management methodologies guarantees enhanced productivity, cost-efficiency, and streamlined operational processes. In addition to their technical expertise, construction managers serve as exemplars of responsibility and professionalism. By adhering to elevated ethical principles, individuals demonstrate their ability to traverse intricate choices with honesty and sincerity, thereby guaranteeing equity, openness, and responsibility in all transactions. Furthermore, the establishment of ethical behavior serves as the fundamental basis for the process of making decisions, cultivating a culture that prioritizes honesty, impartiality, and responsibility. This paper thoroughly examines the multifaceted aspects of a construction manager's responsibilities, emphasizing their crucial contributions towards the advancement and maintenance of safety standards within the construction sector.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
A Construction Manager (CM) is a technically proficient individual responsible for supervising the strategic organization, synchronization, and implementation of building initiatives, commencing with the first idea through the finalization of the work. This position requires a thorough comprehension of development methodologies, concepts of engineering, and strategies for managing projects (Maqbool and Amaechi, 2022). Construction managers (CMs) play a crucial role in facilitating effective communication and coordination among architects, engineers, contractors, plus customers. Their primary objective is to guarantee that projects are completed within the designated timeframe, adhere to the allocated budget, and meet the strictest requirements of quality.
It is common for managers of construction to hold advanced degrees in construction management, engineering, or related disciplines.
Project Organizing: Construction Managers team up with design and structural experts to lay out a thorough procedure at the beginning of a project. They team up to create comprehensive plans and timetables for the development interaction.
Group Management: Construction employees, including subcontractors, project workers, and laborers, are under the oversight of Construction Managers, who are entrusted with planning and checking the entire effort (Ghorbani, 2023). Their essential objective is to cultivate powerful correspondence and smooth coordinated effort among teammates.
Quality Control: Construction Managers are liable for maintaining exclusive requirements of value in project developments (Shayan et al. 2022). They do this by performing regular inspections of construction sites to guarantee consistency with primary and specialized necessities.
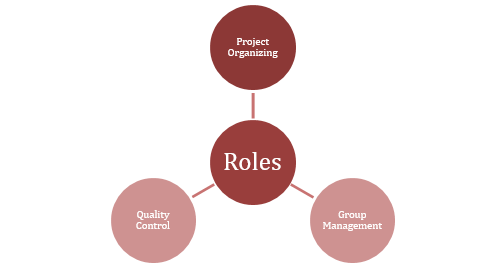
Figure 1: Roles of Construction Manager in Construction Site
(Source: Self-created on MS word)
Controlling Expenses: Construction managers are responsible for overseeing project budgets (Gao, 2022). Which involve the management of spending, negotiation of arrangements, and the optimization of resources in order to minimize the risk of exceeding the allocated funds.
Managing Risks: Construction managers are responsible for identifying prospective hazards, formulating backup strategies, and effectively managing unanticipated hurdles in order to maintain project progress and overcome barriers (Shayan et al. 2022).
Client Interaction: The responsibilities of the construction manager will include acting as the principal connection for clients (Adekunle et al. 2022). Ensuring consistent communication, handling any issues or inquiries, and effectively maintaining what clients want.
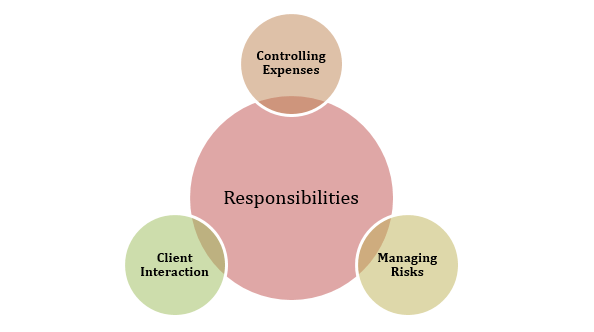
Figure 2: Responsibilities of Construction Management on Construction Site
(Source: Self-created on MS word)
The possibility of shifts occurring in expenses as well as the accessibility of building supplies has an opportunity to create problems to project schedules and expenditures (Han et al. 2023). As a result, construction managers are required to swiftly determine and secure various sources in order to avoid these disruptions.
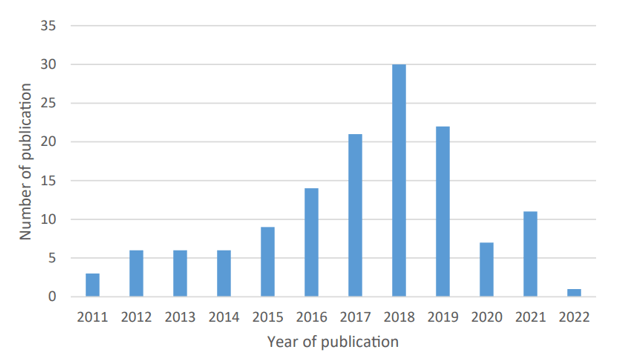
Figure 3: Trends of publications in prefabricated construction supply chain
(Source: Han et al. 2023)
Maintaining a condition of perpetual surveillance is essential for ensuring the successful administration of complex and ever-changing building regulations, authorizations, and environmental standards (Krechowicz, 2022). This is necessary in order to avoid the possibility of being involved in any possible legal conflicts.
The fact that there is a shortage of skilled workers in the construction industry has the possibility of delaying the progression of projects (Ni et al. 2022). As a result, it is necessary to use novel ways to recruit employees and to build projects that seek to enhance the skills of the workforce as a whole.
Construction managers use a variety of advanced management methodologies to effectively handle the complicated tasks associated with building projects. These strategies play a crucial role in guaranteeing the quick completion of projects while adhering to budgetary constraints and upholding the finest requirements for performance.
The Critical Path Method is a project management technique that employs an algorithm of math to generate a comprehensive project plan (Bhatt et al. 2022). That delineates the order of operations, their respective durations, and the interdependencies among them.
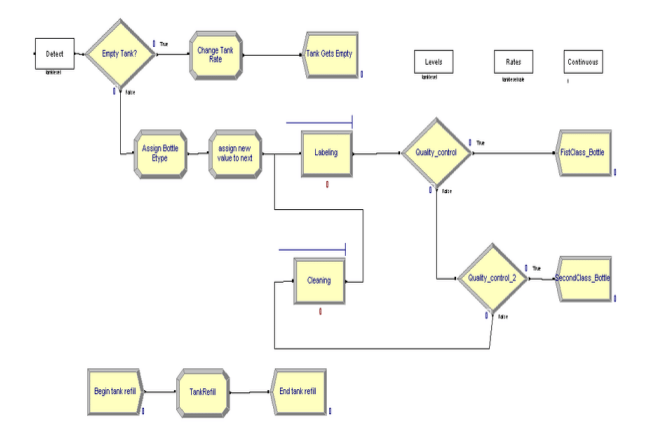
Figure 4: Critical Path method in Arena Simulation Software
(Source: Bhatt et al. 2022)
Construction managers use the Critical Path Method as a means of identifying the most crucial jobs within a project.
Lean construction strategies are centered on the objective of optimizing productivity and decreasing wastage across the whole of the building process (Rashidian et al. 2023). Construction managers use lean concepts in order to optimize procedures, remove tasks that do not add value, save expenses, and improve project efficiency.
Building Information Modeling refers to a comprehensive digital depiction of an architecture’s interior and operational features (Parsamehr et al. 2023). Building managers use Building Information Modeling to successfully represent the whole building management.
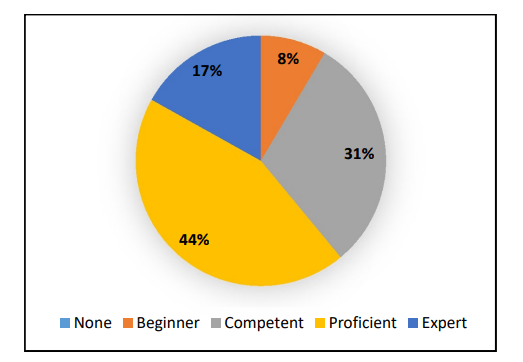
Figure 5: Level of understanding of BIM
(Source: Sami et al. 2022)
Proactively detect possible confrontations or concerns prior to their occurrence, foster cooperation among various stakeholder groups, and promote project-wide collaboration and productivity.
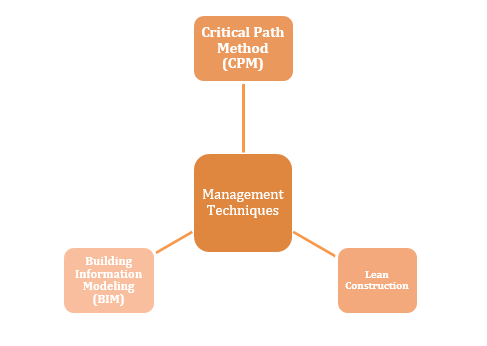
Figure 6: Management Techniques of Construction Managements
(Source: Self-created on MS Word)
The use of efficient management strategies has been shown to improve the processes of preparing, organizing, and implementing (Shojaei, and Burgess, 2022.). Through the optimization of operations and the proper division of resources, construction managers play a crucial role in ensuring the timely completion of activities, hence minimizing the overall length of an undertaking and the related costs.
The use of demanding management practices has been shown to enhance the effectiveness of quality assurance processes. Construction managers possess the ability to effectively oversee construction procedures, guaranteeing that the work performed conforms to standards set by the industry and fulfils the expectations of clients.
The use of efficient management procedures facilitates the precise calculation, financial management, and monitoring of costs. Construction managers possess the ability to discover potential cost-saving options, effectively mitigate budget overruns, and skillfully negotiate advantageous agreements with manufacturers and third-party vendors.
Insufficient management has the potential to result in project postponements as a consequence of ineffective time management, insufficient collaboration, or the failure to swiftly handle unanticipated challenges (Suleiman, 2022). Slowdowns in building work may lead to financial implications, strain relationships with consumers, and negatively impact the image of a construction company.
Poor management often leads to imprecise spending, incorrect utilization of assets, and excessive expenditure. This phenomenon has the potential to exert pressure on monetary resources, result in cutbacks in the project dimension, affect the quality of the project, and give rise to conflicts among stakeholders.
Insufficient management and insufficient communication have the potential to undermine the general standard of work (Gamil, and Rahman, 2023). The presence of inadequate focus on specific aspects, absence of comprehensive quality assurance measures, and ineffective communication may lead to the need for more work, the occurrence of flaws, and the emergence of safety risks, compromising the overall soundness of the building endeavor and perhaps exposing the involved parties to legal obligations.
Ethics represent the foundational principles that construction managers rely on to navigate their conduct, choices, and professional relationships throughout the construction industry. Maintaining a stringent ethical framework is vital in an industry where confidence, transparency, and responsibility hold the utmost significance (Oladinrin et al. 2023). Construction managers are obligated to adhere to a set of ethical norms including honesty, openness, impartiality, and consideration for all parties engaged in a given project. These principles serve to guarantee the ethical and effective execution of projects, therefore creating an atmosphere characterized by trustworthiness and reliability.
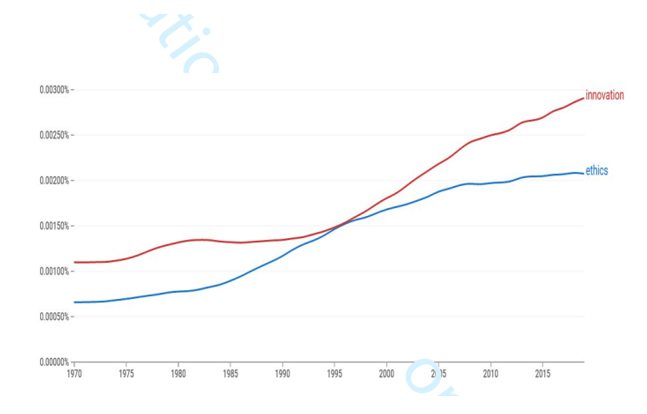
Figure 7: Frequency of the terms’ ethics’ and ‘innovation’.
(Source: Oladinrin et al. 2023)
The demonstration of positive ethical behaviors by construction managers plays an essential part in fostering cooperation within the construction industry (Almashhadani et al. 2023). The adherence of construction managers to ethical standards fosters an environment that is favorable for transparent communication, collaboration, and collaboration throughout a wide range of stakeholders, such as construction workers, engineers, architects, and customers.
The practice of ethical conduct fosters the development of goodwill between members of the team and stakeholders. Enhanced confidence in the construction manager's decision-making and behavior fosters improved cooperation, leading to increased efficiency and effectiveness.
Proficient ethical construction management has the expertise to effectively address issues in an impartial and equitable way. By effectively and impartially resolving conflicts, individuals create an environment that promotes open communication and mutual respect, therefore motivating members of the team to collaborate cohesively in pursuit of project objectives.
The promotion of ethical conduct fosters a climate that values and supports transparent and truthful engagement. Construction executives who follow to ethical principles demonstrate approachability, attentive listening skills, and a genuine appreciation for the perspectives and views of their team workers (Regúlez et al. 2023). The aforementioned transparency facilitates the dissemination of information, hence promoting a shared understanding among all stakeholders with regard to the progress and obstacles encountered in the project.
Ethical managers of construction place a high priority on addressing the requirements as well as worries of every stakeholder involved in a building project. By taking into account a range of viewpoints and exhibiting understanding and compassion, individuals create a cooperative atmosphere in which all parties involved feel appreciated and respected. The use of an inclusive strategy has been shown to result in enhanced choice-making and outcomes for the project.
The implementation of work-at-height rules is of utmost importance within the construction business, as they serve as crucial safety recommendations. Their primary focus is on engaging in tasks that require working at elevated heights (Meidia et al. 2023). With a strong emphasis on the avoidance of slips. Restrictions pertaining to construction areas are of utmost importance due to the presence of people engaged in tasks at different elevations.
Ensuring adherence to work-at-height rules requires the meticulous arrangement, oversight, and implementation of activities (Kumar et al. 2023). Various preventative actions, including the installation of barriers, security nets, and the provision of individual fall-prevention devices, are done with the aim of averting disasters. The strict observance of these standards has a substantial impact on mitigating the occurrence of falls, hence safeguarding the well-being of employees and decreasing the occurrence of accidents. Construction managers play an important part in the enforcement of these requirements since they are responsible for performing routine site inspections, supplying essential protective gear, along guaranteeing all employees get sufficient training in activities linked to working at heights.
The primary objective of the Manual Handling Operations Regulations is to prevent harm to employees from the potential hazards linked to manual handling tasks, including the carrying, lifting, pulling, or transporting of substantial weights. Inadequate execution of methods involving manual labour has the potential to result in the development of muscle-related illnesses and enduring damage, therefore exerting a detrimental effect on the physical and mental health of workers, as well as impeding the overall effectiveness and productivity of building endeavours (Awolusi et al. 2018). The rules mentioned above place significant emphasis on the need to conduct risk assessments, provide appropriate training, and use mechanical assistance in order to mitigate the physical strain experienced by employees. Construction managers have the duty of recognizing the physical handling jobs that occur on the building premises, doing risk analyses, and adopting control mechanisms to mitigate potential hazards. Construction managers play a crucial role in reducing physical handling-related accidents by implementing measures such as instructing employees in secure lifting procedures and equipping them with mechanical assistance such as carts and cranes.
Construction managers serve a crucial and essential role in the effective management and oversight of the safety and health protocols inside construction sites. The roles of construction managers consist of:
Construction managers are responsible for coordinating safeguarding instruction for employees, with the aim of assuring their awareness of the potential hazards connected with the assigned activities and providing them with the necessary training in safety practices (Lundberg et al. 2022). The use of ongoing learning initiatives fosters an employee that prioritizes safety.
Construction managers carefully implement security and health requirements. The organization ensures that employees conform to safety protocols, including the use of suitable personal protection equipment, adherence to security protocols, and compliance with rules pertaining to tasks involving elevated positions, laborious handling, and other operations associated with high levels of risk.
Construction managers undertake periodic visits to the site to detect possible dangers and verify the implementation of security protocols. Prompt and quick remedial measures are implemented in response to any instances of violations.
Construction managers are responsible for supervising the presence and effectiveness of security supplies at the construction site, therefore guaranteeing that all workers are equipped with appropriate personal protective gear (May et al. 2022). Ensuring the safety of employees is achieved by the implementation of periodic assessments, timely repairs of broken goods, and thorough management practices. The heightened level of attentiveness shown by workers contributes to a decrease in accidents, underscoring the need to prioritize employee security within the building sector.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, construction managers play a crucial role in the construction sector by using efficient interpersonal and leadership strategies to facilitate smooth cooperation among members of the team. The individuals in question adeptly negotiate complex ethical quandaries, prioritizing the principles of justice, openness, and respect in all decision-making processes. This approach fosters a sense of confidence and commonality throughout the building community. Moreover, their extensive comprehension of safety and health regulations, specifically in domains such as elevated work and physical labor tasks, reinforces building sites from possible hazards, ensuring the protection and welfare of the personnel. Furthermore, construction managers have a crucial role in promoting innovation, using state-of-the-art technology and integrating sustainable methodologies. The capacity of individuals to adjust to changing industry trends improves the effectiveness of projects and reinforces environmental stewardship, so linking construction endeavors with worldwide sustainability objectives. Construction managers play a pivotal role in overseeing construction projects, but their responsibilities extend beyond basic supervision. They are crucial in designing and cultivating construction ecosystems that prioritize safety, ethics, and sustainability. The essential role played by the individual in question is shown by their unwavering commitment to preserving industry standards, fostering a culture of cooperation, and prioritizing the well-being of workers. The importance of construction managers in creating a flexible, accountable, and cooperative business cannot be stressed as the industry is still in evolution. The influence of their work extends beyond the physical buildings they construct, including an enduring heritage characterized by professionalism, safety, and honesty. Construction managers play a pivotal role in shaping the next phase of construction administration, ushering in a new era characterized by advancements in innovation, ethical practices, and enhanced safety measures within the construction industry.
Reference list
Journals
Websites
Introduction Get expert insights on IHRM strategies and hybrid work models with our reliable assignment helper, ensuring...View and Download
Introduction Rapid Assignment Help is your one-stop shop for expert guidance and reliable Assignment Help for every...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction Get Free Online Assignment Samples from UK's Best Assignment Help Experts to boost your academic...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking assignment help uk from Rapid Assignment...View and Download
Copyright 2025 @ Rapid Assignment Help Services
offer valid for limited time only*

