+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
Get ahead in your academic journey with Rapid Assignment Help, your trusted provider of exceptional Assignment Help Online solutions.
The construction industry remains a foundation of present-day culture, with the formation of many-sided designs and framework projects shaping the regular routines. At the core of these undertakings is the development supervisor, an essential figure liable for coordinating the mind-boggling orchestra of exercises that change structural plans into substantial, useful real factors. The job of a construction manager is diverse, requiring a wide range of abilities and a deep comprehension of the development cycle. Their essential obligation is to guarantee that tasks are finished on time, inside a financial plan, and to the best expectations of value and security. From beginning to end, development directors are engaged with each period of an undertaking, giving oversight, direction, and dynamic mastery.
One of the central jobs of a development chief is to collect and lead a durable group of experts, including modellers, designers, subcontractors, and workers. Compelling authority and openness are vital administration strategies that empower them to organise the different partners, cultivating joint effort and keeping everybody lined up with project targets. Construction Managers should be knowledgeable in project arranging and booking, asset portion, risk the executives, and cost control. These administration strategies are fundamental for effective undertaking execution. They utilize apparatuses like the Critical Path Method (CPM) and project the board programming to make exhaustive venture plans and to screen progress, making fundamental changes as difficulties emerge.
A construction manager (CM) is a professional who oversees and manages construction projects from conception to completion. They act as the agent of the project owner or developer and are responsible for planning, coordinating, budgeting, and supervising various parties like architects, engineers, contractors, and suppliers. The role requires strong leadership, organizational, communication, and problem-solving skills (Alhammadi, 2019). CMs need extensive knowledge of construction materials, methods, regulations, contracts, and safety procedures. They are involved throughout the project lifecycle - from feasibility studies and design, tendering and contracting, to execution, monitoring progress, quality control, troubleshooting issues, and final handover.
Figure 1: Construction Management Skills
The key roles of a construction manager
Construction managers encounter various challenges on the job. Managing complex projects within strict time and budget constraints (García de Soto et al. 2022). Delays can increase costs. Coordinating numerous contractors, suppliers, and specialists, and maintaining harmony. Conflict resolution skills are vital. Ensuring safety and compliance with regulations on-site to prevent accidents and penalties. Adapting to changes in scope, unforeseen conditions, resource availability, and external factors like weather. Requires contingency planning. Meeting quality standards despite pressures. Quality control is paramount. Updating knowledge and skills to keep the rate of new construction methods, regulations, contracts, and technological tools. Requires continuing education. High-stress working environment with long hours and tight deadlines can take a toll on work-life balance.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.

Figure 2: Project Management Challenges
Construction managers employ various techniques and skills for the smooth execution of projects. Motivating and influencing the project team to meet objectives. Promoting collaboration through clear direction, open communication, and fair treatment. Prioritizing tasks, multi-tasking, and allocating resources efficiently. Using scheduling tools like Gantt charts, CPM, and PERT networks. Tracking actual costs against estimates through methods like earned value analysis. Controlling changes via proper change order management. Systematic planning and execution to meet quality standards (Ghorbani, 2023). Using tools like Total Quality Management (TQM), quality audits, and ISO certification. Establishing safety policies and procedures. Ensuring compliance through training, inspections, incident reporting, and enforcement. Promoting a safety-first culture. Identifying, analyzing, and responding to project risks. Using techniques like SWOT analysis, probabilistic analysis, and simulation. Developing contingency and mitigation plans. Preventing and resolving claims and conflicts through proper documentation, negotiation, mediation, arbitration, and litigation. Leveraging construction management software, Building Information Modeling (BIM), drones, and IoT sensors for better data, control, and decision-making.
Effective management techniques offer construction managers several benefits.
Figure 3: Key management of construction management
Construction managers have an ethical responsibility to be honest, transparent, and accountable in all business dealings. Avoid bribery, falsification, and concealment of facts. Make fair judgments and avoid preferential treatment based on personal relationships or favors. Award contracts impartially. Uphold technical and moral standards of the profession. Continuously improve through education and experience sharing. Ensure designs, materials, and methods address both safety and sustainability adequately. Protect sensitive information like bid details, and contract awards before official announcements (Lee and Kang, 2020). Honor intellectual property. Avoid situations where personal interests may compromise professional judgment or obligations.
Moral contemplations in the development of the board are instrumental in molding the ways of behaving of development chiefs in the work environment. These standards are imperative for keeping up with proficient trustworthiness as well as adding to the general outcome of development projects. Development directors are supposed to be straightforward and legitimate in the entirety of their dealings (Lundberg et al. 2022). This includes giving exact data to clients, subcontractors, and colleagues. Moral conduct in such a manner guarantees that partners can believe the data and choices made during the venture. Development chiefs should persistently oversee and reveal any expected irreconcilable circumstances.
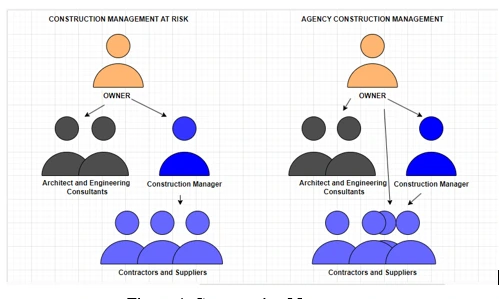
Figure 4: Construction Management
A positive moral way of behaving is a foundation of powerful joint effort inside development undertakings, and it fundamentally impacts the way of behaving of development chiefs in the work environment. Positive moral way of behaving, like genuineness, honesty, and straightforwardness, cultivates trust among colleagues and undertaking partners. Set clear goals, roles, and responsibilities of each party at the project outset. Maintain transparent communication and feedback channels. Make objectively timely, equitable decisions and commitments regarding scheduling, payments, change orders, etc. Implement quality assurance systems applied evenly to all parties (Newman et al. 2021). Acknowledge the good work and extra efforts of team members. Mediate disputes through open dialog rather than lawsuits. Build relationships based on mutual trust and respect rather than fear or favors.
Developing supervisors who reliably show these ways of behaving construct a standing for believability. At the point when partners trust the development supervisor's statement and activities, it prompts smoother joint effort. Trust diminishes the probability of questions and improves the eagerness of colleagues to cooperate. Moral conduct in the work environment involves approaching everybody with deference and advancing inclusivity. Development chiefs who maintain these standards establish a climate where different viewpoints are esteemed. In cooperative tasks, various partners bring shifted aptitudes, encounters, and thoughts to the table. At the point when all voices are heard and regarded, it supports advancement and better critical thinking, eventually helping the venture.
Working at height is a major risk in construction. A hierarchy of controls must be followed - eliminate, prevent falls, and minimize height/impact. Ladders, scaffolds, and platforms must be appropriate, secured, and not overloaded (Noor et al. 2020). Fall arrest systems like safety nets and harnesses must be used if fall risk exists. Inspections before use and at intervals. Records maintained. Training on risks, procedures, equipment use, and inspections. Safe zones and barriers are established to prevent objects from falling. Head protection must be worn in all cases. Falls from height are a major cause of serious and fatal injuries in construction. Standards minimize risks through proper equipment, planning, and training.
Periodic inspections ensure equipment condition does not deteriorate with use. Barrier and zone controls protect both workers at height and anyone at lower levels. Mandatory use of personal fall arrest systems acts as the last line of defense. Work at Level Guidelines 2005 is a pivotal regulation in the development business, stressing the need to evaluate and limit gambles while working at levels. The significance of these guidelines lies in keeping tumbles from level, which are a main source of fatalities and wounds in development (Thanh Phan and Nguyen, 2022). These guidelines require an efficient way to deal with overseeing work at the level, including risk evaluations, wellbeing estimates like guardrails and bridles, and legitimate preparation for laborers.
The Manual Taking Care of Tasks Guidelines 1992 means to safeguard laborers from the dangers related to manual dealing with exercises, which are normal in the development area. These guidelines are indispensable as manual dealing with wounds represents a critical part of development-related mishaps (Phan and Nguyen, 2022). They expect bosses to evaluate errands including manual taking care of, execute controls to lessen gambles, and give preparation to laborers on safe lifting procedures. Consistency with these guidelines limits the gamble of outer muscle problems and different wounds. Eliminate or minimize manual handling through the use of automation, tools, and breaking loads into smaller units. Assess risks considering weight, shape, path, and individual capability. Plan lifts accordingly.
Using appropriate gear like trolleys, and hoists. Provide adequate rest periods. Train workers on safe handling techniques - posture, grips, and team coordination. Set permissible limits for load weight, and repetitive lifts based on ergonomic studies. Ensure the ground is even, stable, and clear of obstructions. Mark heavy load centers of gravity if offset. Encouraging mechanization and smaller loads to reduce injury risks. Assessing task risks through systematic analysis rather than assumptions (Sukri and Rahman, 2023). Providing proper tools and PPE tailored specifically to the handling task. Training workers on ideal movements and postures to prevent strains. Setting limits on weights handled and lift frequencies based on human capacity. Ensuring the external environment does not add to injury risk.
The construction manager is responsible for ensuring health and safety on site. Including safety requirements in contracts to legally bind contractors. Reviewing and approving contractor safety plans before work begins (Sampaio et al. 2023). Conducting frequent inspections and audits of site conditions, practices, and equipment. Verifying competence and providing additional training to workers. Maintaining safety records and incident reports to identify patterns. Intervening proactively if risks are observed and stopping work if serious violations or hazards are found. Promoting safety culture through incentives, leading by example, and enforcing policies. Liaising with external health and safety authorities for reviews and investigations. Development administrators are liable for recognizing likely dangers, for example, working at level and manually dealing with assignments, and leading intensive gamble appraisals. This cycle helps in deciding the essential well-being measures and controls. Development directors should guarantee that the building site follows all pertinent well-being and security guidelines, including the Work at Level Guidelines and Manual Taking Care of Activities Guidelines.

Figure 5: Healthy and Safety Policies
This includes remaining refreshed on any progressions in regulation. Development supervisors administer the preparation of laborers, guaranteeing they comprehend the significance of well-being measures and are skilled in their utilization. They likewise give oversight to guarantee safe work rehearses are followed. Viable openness is of the utmost importance. Development chiefs need to convey well-being assumptions, guarantee laborers know about possible dangers, and keep an open channel for revealing security concerns (Sarpin et al. 2021). At the point when mishaps or close misses happen, development directors assume a critical part in occurrence revealing and examination, assisting with forestalling repeats. Development supervisors should show others how it's done, exhibiting a promise of well-being and security. This impacts the general security culture of the building site.
F. Conclusion
In summary, construction managers have a vital role in delivering projects successfully. They manage diverse specialists, balance priorities like cost, schedule, and quality, and create a collaborative yet controlled environment. Ethics, health, and safety are paramount in construction, so managers must establish and maintain proper systems for transparency, hazard mitigation, and regulatory compliance. With the pressures inherent in construction, managers must hone their technical and leadership skills to optimize results. The role is challenging but critical in turning conceptual designs into physical reality within limited resources. Compelling administration procedures used by development supervisors assume a significant part in forming the results of development projects. While there are clear benefits to utilizing these strategies, recognizing the intrinsic difficulties and disservices that go with the job is fundamental.
On the positive side, these methods empower development administrators to advance asset usage, guaranteeing that materials, gear, and work are effectively conveyed. This productivity means projects being finished on time and inside the financial plan, a basic consideration of the development business' intensity and benefit. Viable administration methods likewise act as a safeguard against expected chances. Development chiefs who are adroit at distinguishing, surveying, and alleviating gambles add to the counteraction of expensive postponements, accidents, and questions. Besides, the emphasis on clear correspondence and joint effort innate in these procedures cultivates collaboration and arrangement among project partners, prompting better critical thinking, upgraded proficiency, and smoother project execution. It is significant to perceive the drawbacks that development chiefs might experience. The persistent strain and stress of overseeing complex tasks can prompt burnout and unfavorable well-being impacts, influencing the two people and undertaking results. Spending plan invades stay a steady danger, as incapable administration strategies can prompt monetary misfortunes and upset project maintainability.
Reference List
Journals
Introduction Growth planning is defined as continuous business planning procedure which aids businesses to be concentrated, grow...View and Download
1.0 Introduction: GUL’s Kinetic Activity Research Lab Thе Faculty of Enginееring Sciences at Global University London...View and Download
Introduction Explore free assignment samples crafted by our subject experts and take advantage of our online Assignment Helper...View and Download
1. Introduction: Mancala Game Implementation for CMSC 201 The Mancala Game project is an attempt to design and develop a...View and Download
Introduction: Understanding Life Expectancy and Health Life expectancy is defined as the measure that assists in evaluating...View and Download
Introduction - Consulting in Practice Portfolio Elevate your academic performance with our personalized Assignment Help, created...View and Download
