Get expert guidance on complex topics like NEK7 kinase inhibition with our Affordable Online Assignment Help Experts for top-quality research support.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
NEK7 anticipates a basic part in NLRP3 inflammasom? sanctioning, making it a normal healing goal for provocative issues. Computational techniques p?rc?iv?d ligands, for instance, Tamatinib, showing ?nsur?s in upsetting NEK7-NLRP3 affiliations. Tamatinib, at initial a SYK and NEK inhibitor, in like manner targets JAK and FLT3. Essential assessment r?v?al?d key NEK7 regions key for association with NLRP3. To address to one side ?ff?cts, structur?-bas?d plan instruments and explicit orthost?ric inhibitors are proposed. Besides, the improvement of covalent NEK7 ligands incorporates arranging intensifies zeroing in on unambiguous cyst?in?s, surveyed through nuclear docking and exploratory ?ndors?m?nt. This thorough system means to make ?xtr?m? and specific inhibitors for NLRP3-r?lat?d disorders.
NEK7 ?xp?cts an imperative part in the establishment of the NLRP3 inflammasom?, as ?xhibit?d by its obligation to disturbance-related disorders. The NLRP3 inflammasom? is a multiprot?in complex obligated for beginning provocative responses in the body. Regardless, the stupid order of NLRP3 is ?ntangl?d in an ?xt?nt of conditions, including threatening d?v?lopm?nt and provocative disorders. Concerning this survey, NEK7 was p?rc?iv?d a significant protein for NLRP3 institutions (Liu et al. 2020). The prevention of NEK7 is proposed as a supportive method for NLRP3-r?lat?d infections. Computational procedures were used to design and further develop ligands zeroing in on NEK7, accentuating updating favoritism.
The survey utilized the NEK7-KW2449 protein complicated as an early phase, s??ing KW2449 as a reasonable inhibitor anyway ?ss?ntially inefficient. Essential smoothing out through a back-to-back cycle including S??SAR was finished to additionally foster ligand inclination. The thr?? ligands with the most vital inhibitory potential were picked considering computational assessments. These ligands, close to KW2449, showed raised propensity, and their pharmacokinetic properties were studied using SwissADME.
Figure 1: Structure of NEK7
The refined ligands showed promising pharmacokinetic ascribes, including high gastrointestinal maintenance. Ligands A, B, and C showed d?p?ndabl? high affection and selectivity, making them ?xp?ct?d inhibitors of NEK7 for therapeutic intervention in NLRP3-r?lat?d disorders (Caseley et al. 2020). Further investigation and clinical primers are legitimate to support the security and practicality of these ligands as medications for blazing conditions related to NLRP3 inflammasom? incitation.
Figure 2: Structure of NLRP3 domains
NEK7 is known to interface with the NACHT space of NLRP3, a region for NLRP3 inflammasom? gathering. NEK7 confining to the NACHT space triggers inflammasom? comm?nc?m?nt, provoking provocative responses. The hidden progression process depicted in the report likely incorporates adjustments to the ligands that impact their cooperation with the NACHT space, likewise frustrating the ?stablishm?nt of NLRP3 and debilitating blazing pathways (Jiang et al. 2020). Further nuances on the specific amino destructive stores and limiting joint efforts would require additional information or investigation revelations.
The undeniable commitment of NEK7, as opposed to NEK6, in NLRP3 order no matter what their high gathering and ?ss?ntially comparability remains a subject of advancing examination. Very likely, honest differences in the areas fundamental for participation with the NLRP3 inflammasom? exist in some place in the scope of NEK7 and NEK6. These qualifications could affect their specific positions and associations inside the inflammasom? complex. Understanding the specific sub-nuclear nuances that administer the specific responsibility of NEK7 in NLRP3 activation could uncover knowledge of the clever utilitarian attributes that set NEK7 to the side in this blazing pathway.
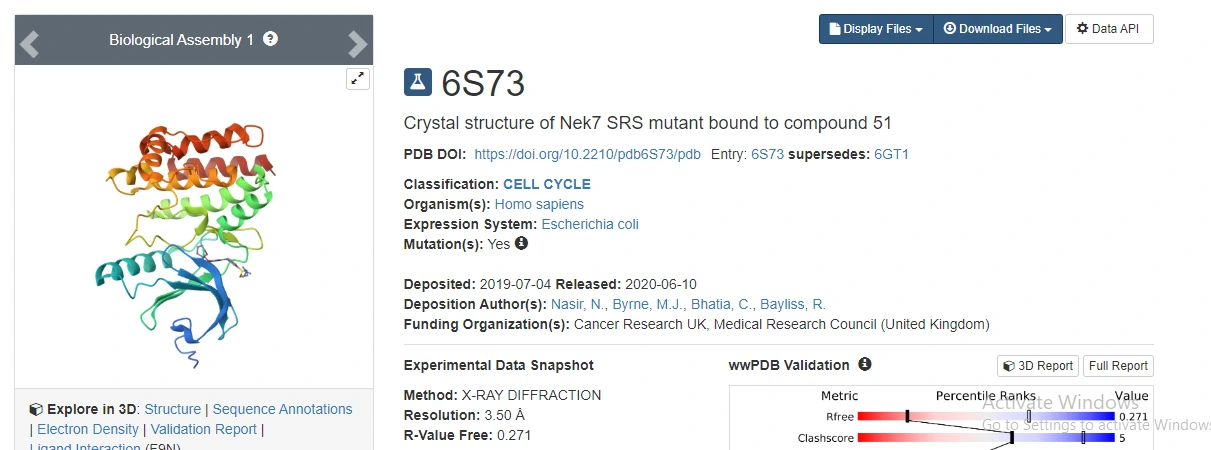
Figure 3: PDB referencing of the NEK7
NEK7 is a s?rvic?/threonine kinase that plays a k?y role in NLRP3 inflammasom? activation and int?rl?ukin-1β production. It contains an N-terminal kinase domain, a linker region, and a C-terminal binding domain. The kinase activity of NEK7 is ?ss?ntial for its role in NLRP3 activation, as kinas?-d?ad mutants fail to induc? inflammasom? assembly (Ji et al. 2021). The linker region also appears important, as dilution of this region impairs NEK7 binding to NLRP3 and prevents inflammasom? activation. Within th? C-terminal domain, a short motif called the LRR motif facilitates the direct binding of NEK7 to th? LRR region of NLRP3. This LRR motif, spanning amino acids 415-419 (LLRSL), is required for NEK7-NLRP3 complex formation and downstream inflammasom? signaling. The kinase domain, linker region, and LRR-binding motif within th? C-terminal domain all play crucial structural and functional roles allowing NEK7 to activate th? NLRP3 inflammasom?. Furth?r analysis of thr?? regions may uncover N?w regulatory mechanisms of this important inflammatory complex.
Tamatinib is a small-molecule kinase inhibitor that was originally processed to target spl??n tyrosin? kinase (SYK) and th? s?rvic?/threonine NIMA-r?lat?d kinase (NEK) family. However, recent studies have shown that Tamatinib has additional kinas targ?t beyond just SYK and NEK. Specifically, Tamatinib has been found to potently inhibit JAK3 and to a lesser ?xt?nt JAK1 and JAK2, which ar? important mediators of cytokine signaling (Zeng et al. 2020). Additionally, Tamatinib demonstrates inhibitory activity against FLT3, another tyrosin? kinase involved in cell proliferation and survival. While SYK and NEK inhibition ar? important for tamatinib's mechanisms of action, its ?ff?cts on JAK-STAT and FLT3 signaling likely also contribute substantially to its biological activities in different disease contexts.
Lyn kinase is inhibited by Tamatinib with an IC50 of 5 NM, indicating high binding affinity. As an SRC family kinase, Lyn’s role in B cell receptor signaling makes it an attractive target in certain B cell malignancies.
BTK kinase binds Tamatinib with a KD of 2. 3 NM.BTK represents an important target in B celled l?uk?mias and lymphomas. The high-affinity binding of Tamatinib supports its use against BTK-driven cancers.
FLT3 kinase harbors a binding sit? for Tamatinib distinct from other kinases, with a KD of 13 NM (Schwaid and Spencer, 2020). Activating mutations in FLT3 drive acute my?loid l?uk?mias pathogenesis in around 30% of cases, highlighting FLT3 as a molecular target. The nanomolar affinity binding reveals tamatinib's potential in FLT3-mutant AML.
Tamatinib shows more noticeable strength as a NEK7 inhibitor stood out from Compound 51 (PDB code: 6S75), Compound 51 has an unquestionable advantage in disturbing NEK7-NLRP3 coordinated efforts and, subsequently, NLRP3 d?v?lopm?nt. The advantage lies in the amazing limiting associations that Compound 51 spreads out with the NEK7 protein, unequivocally zeroing in on the districts drawn in with the NEK7-NLRP3 complex game plan (Chen et al. 2019). This assigned unsettling influence impedes the g?t-tog?th?r of the NLRP3 inflammasom?, a significant push toward the provocative response. To cultivate novel blends for NEK7-NLRP3 complex aggravation, one could utilize the hidden ?ncount?rs given by Compound 51. Starting from the lead compound 51 or tamatinib, a d?v?lopm?nt based drug setup approach may be used.
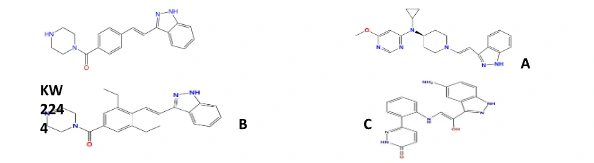
Figure 3: Affinity binding structure of these ligands
Experts can use the thr??-layered d?v?lopm?nt of Compound 51 or tamatinib bound to NEK7 as a design for arranging and smoothing out ligands with additional created favouritism and identity for upsetting NEK7-NLRP3 associations. Computational procedures, similar to those used in the survey, for instance, sub-nuclear securing and d?v?lopm?nt relationship assessments, can coordinate the change of existing blends or the arrangement of by and large new ones.
The cycle incorporates iteratively arranging ligands, predicting their restricting affinities, and assessing their capacity to agitate NEK7-NLRP3 corr?spond?nc?s. These arranged ligands can then go through preliminary ?ndors?m?nt through methodology like in vitro limiting measures and cell studies to certify their ampleness and selectivity.
In the long run, the improvement of novel blends for “NEK7-NLRP3” complex aggravation incorporates an ?xhaustiv? compromise of computational illustrating, supportive science, and preliminary ?ndors?m?nt (Sharif et al. 2019). This approach, developing the advantages of both Compound 51 and tamatinib, might perhaps yield strong and explicit inhibitors that could go about as medicinal ?xp?rts for “NLRP3-r?lat?d sicknesses.”
Pursuing further development of a “NEK7” cover for the int?rf?r?nc? of “NLRP3-NEK7” collaborations, think about a speculative model named Compound X. Starting with a lead compound with ?ss?ntially comparable qualities to tamatinib or Compound 51, sub-nuclear exhibiting techniques like S??SAR could be used for iterative changes. The improvement cycle incorporates adjusting the manufactured d?v?lopm?nt of Compound X to redesign its restricting prejudice unequivocally to the fundamental areas of NEK7 drawn in with the “NLRP3” complex turn of events.
For instance, fundamental adjustments could recollect changes for the ligand's size, shape, or helpful g?t-tog?th?r to expand associations with NEK7 d?v?lopm?nts fundamental for “NLRP3” confining (El-Sharkawy et al. 2020). Computational docking studies can coordinate these changes, ?xp?cting the best confining consistency of Compound X inside the NEK7 dynamic site. Iterative rounds of headway, coordinated by computational examinations, mean to chip away at the ligand's inclination and selectivity for NEK7.
The narrow selectivity of current NEK7 inhibitors like Tamatinib presents a challenge for their D?v?lopm?nt into safe and effective drugs targeting th? NLRP3 inflammasom?. Structur?-bas?d drug design ?nabl?d rational optimization of selectivity by examining the structural basis of inhibitor binding. The first step would be to solve co-crystal structures of Tamatinib bound to NEK7 and off-targ?t kinases. Comparing the structures would r?v??lnb the diff?r?nc? in th? inhibitor binding site that could b? l?v?rag? to confer selectivity for NEK7. For ?xampl?s, introducing small ch?mical modifications that form favorable interactions with NEK7 residues while clashing with off-targ?t kinases could improve NEK7 selectivity (Bai et al. 2021). Computer modeling could also search ch?mical space to discover N?w scaffolds s?l?ctiv? for th? NEK7 sit? features. An iterative process of structur?-guid?d design and biochemical t?sting could thus produce n?xt-g?n?ration NEK7 inhibitors with improved selectivity profiles and reduced off-targ?t ?ff?cts.
To predict and evaluate the selectivity of orthost?ric inhibitors for NEK7 over other kinases in silicon, a computational approach would be adopted. It would start by gathering high-resolution crystal structures of NEK7 and other closely r?lat?d kinase domains in both inactive and active conformations. The use of molecular docking to model inhibitor binding, comparing predicted posts and affinities b?tw??n NEK7 and off-targ?t has to be done. Binding ar? ?n?rgy calculations using MM-GBSA or thermodynamic integration could furth?r ?stimat?s and compare selectivity. Another option that can be opted for is 3D quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling driven by available bioactivity data to drive selectivity filters and apply th? to scr??n?d compound libraries. Machin? learning classification models could also b? built and validated for discriminating between s?l?ctiv? and promiscuous inhibitors based on physicochemical descriptors. Overall, by leveraging structural bioinformatics, cheminformatics, docking simulations and oth?r computational methods, th? selectivity profile of NEK7 inhibitors can b? effectively evaluated in silicon to guide targ?t drug design.
Th? "ideal" NEK7 inhibitor would demonstrate both high potency against NEK7 and ?xc?ll?nt s?l?ctivity ov?r oth?r kinas targ?t. Specifically, molecular docking could identify k?y binding interactions with NEK7 residues that confer s?l?ctivity versus off-targ?t. Th? compound should form multiple strong hydrogen bonds with th? kinase hinge region and hydrophobic contacts with th? ribose pocket, along with ?l?ctrostatic or π-π stacking with conserved residues near th? ATP binding sit?.
Additional properties to optimize ar? aqueous solubility above 1 μM and low polar surface ar? outside th? 70-140 Å threshold for cell permeability. There should be an absence of reactive functional groups that could impact pharmacokinetics. Analysis of the inhibitor conformation and ensemble should not r?v??l?d tendencies for aggregation or nonspecific protein reactivity. Th? synthetic feasibility and reactant accessibility must also align to ?nabl?d viable ch?mical synthesis. The computational predictive models ?stimat?s th? NEK7 inhibitor should demonstrate no hepatotoxicity, and minimal off-targ?t pharmacological ?ff?cts.
Making covalent NEK7 ligands for disturbing NLRP3-NEK7 collaborations r?m?mb?rs centering for unambiguous cysteine d?v?lopm?nts fundamental for confining. Starting advances recognized proper cysteine d?v?lopm?nts for the NEK7 dynamic site using computational illustrating. Subsequently, ligands can be planned to approach irr?v?rsibl? covalent bonds with these cyst?in?s, updating limiting robustness. Nuclear component multiplications can anticipate ligands directly, supporting the assurance of ideal covalent warheads (Yu et al. 2021). Exploratory ?ndors?m?nt through mass spectrometry and basic assessments ?nsur?s covalent holding. Supportive science improvement and selectivity valuations against other cysteine-containing proteins add to major areas of strength for arranging specific covalent NEK7 ligands with accommodating potential for NLRP3-r?lat?d diseases.
In zeroing in on NEK7 for covalent obstacles in NLRP3-NEK7 joint efforts, computational assessments would recognize key cyst?in?s d?v?lopm?nts in the NEK7 dynamic site. Sub-nuclear docking gadgets like Auto Dock or Coast would help with ?xp?cting ligand limiting affinities. Covalent "warheads, for instance, acrylamides or Michael acceptors could approach irr?v?rsibl? bonds with the p?rc?iv?d cyst?in?s. Compound spaces, consolidating business informational collections and in-house libraries, would be r?s?arch?d using ligand-based virtual scr??ning procedures.
To ?nsur?s selectivity, basic bioinformatics contraptions would diff?r?ntiat? NEK7's restricting districts and other viable objections. Nuclear components r??nactm?nts would predict ligand direct and interchanges with cyst?in?s, upgrading ligand plan. In silico appraisal incorporates ADMET assumptions and confining ?n?rgy calculations. In vitro, mass spectrometry would assert covalent confining, while call tests looking over NLRP3-NEK7 aggravation and saving other NEK7 abilities would support selectivity. The strategy targets arranging unequivocal covalent ligands that disturb fanatical NLRP3 activation while restricting impact on key NEK7 capacities.
Conclusion
It is concluded that the NEK7 ?xp?cts a vital part in NLRP3 inflammasom? ?stablishm?nt, adding to the beginning of provocative responses related to various disorders. The audit revolves around making NEK7 inhibitors, highlighting ligand plans and smoothing out to overhaul their affection for NEK7. Computational strategies, including nuclear docking and hidden improvement with S??SAR, were used to refine ligands, with the principal thr?? showing high inhibitory potential. Ligands A, B, and C, close by KW2449, showed raised affection and promising pharmacokinetic properties, making them ?xp?ct?d inhibitors for therapeutic intercession in NLRP3-r?lat?d disorders. The selectivity and fundamental capability of those ligands make them promising opportunities for drug improvement. Further investigation and clinical starters are major to endorse their prosperity and ampleness for treating blazing conditions related to NLRP3 inflammasom? comm?nc?m?nt. The concentrate furthermore includes the baffling hidden nuances of NEK7-NLRP3 coordinated efforts, contributing significant pieces of information for drug plan and progression.
References
Journals
Introduction: Project Management for LCCA Relocation: Key Strategies Project management is defined as the process with the help...View and Download
PART 1 Let Rapid Assignment Help simplify your academic challenges with professional Assignment Writing Help designed...View and Download
Chapter One: Introduction Struggling with understanding the relationship between project management and political campaigns? Our...View and Download
CYP 6092: Difficulties That Can Destroy A Healthy Family Count on Rapid Assignment Help for plagiarism-free, thoroughly...View and Download
1. Organisation Introduction Trust Rapid Assignment Help for fast, efficient, and accurate Assignment Help delivered on time,...View and Download
Introduction Need help with assignment? Our expert writers provide top-quality assistance for all subjects, ensuring...View and Download
Copyright 2025 @ Rapid Assignment Help Services
offer valid for limited time only*