Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment Help services.
“Artificial intelligence” or AI can be defined as technologies or computer programmes, which have intelligence. In the period of the “fourth industrial revolution”, AI is one of the major concerns of all business sectors as well as society. Reason behind the implementation of AI in several sectors is its efficiency and high productivity, which reduces a gap of resources. With the increase in implementation, some concerns are arising such as security, ethical framework, governance and privacy (Schmitt, 2021). There is a need to address these challenges and issues to increase its accuracy and future reliability in business sectors as well as society.
Artificial intelligence has capability process and stores knowledge through its intelligence. The efficiency of AI arises due to its capabilities to acquire knowledge from existing knowledge through analysis and learning. AI has several components such as machine learning and deep learning. Machine learning enhances analysis of real-time data and deep learning enriches learning from the analysis which increases the efficiency and scopes of AI. According to Vähäkainu and Lehto (2019), AI has been introduced with the intention of analysing and investigating challenges and real-life problems as well as resolving them with a human approach. Thus, AI helps in predictive and prescriptive analysis of the factors based on history of events.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
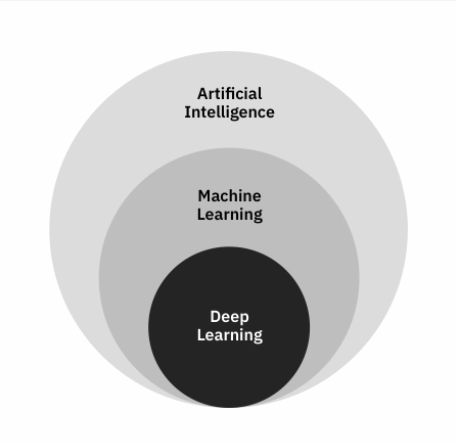
Figure 1: Framework of AI
The term “Confidentiality” can be defined as the process of separation and modification of personal information or data which has been provided by participants, whereas the term “anonymity” is defined as the process of collection of data except for personal information or data (Jivanyan, 2019). Identity refers to “digital identity”. It can be defined as the “collection of identities of computer users. It is effective to identifya user who hasaccess to a system. It is useful to identify unauthentic user of a system and protect confidentiality of private data.
Cyber-attacks are affecting confidentiality of personal data, and have no specific digital identity or anonymous digital identify. Implementation of AI in cyber-security is increasing as because of its quick analysis of data and response through data analysis, which increases the security of data (Ibm.com, 2022a). Due to its efficiency, its usage is increasing over a period of time. New technologies are innovated over period by using AI and deployed in cybersecurity field (Vähäkainu and Lehto, 2019).For example, AI2 platform has been developed to predict cyber-attacks. AI2 has an accuracy of 86% in the identification of cyber-attacks (Vähäkainu and Lehto, 2019).
The intention of cyber-attacks is to breach the privacy of personal information and data of an individual or a business organisation. With the emergence of Industry 4.0, the usage of technologies has increased, which also increased the amount of data and information (Sedjelmaci et al. 2020). Business Assignment Help Cyber security is one of the threats to the privacy of data and information, and AI is effective in analyzing data faster and detecting cyber-attacks. Hence, AI becomes more crucial in the aspect of cyber security.
An ethical framework for AI defines a responsible AI for a business as well as for society (Dignum, 2019). AI has already changed the environment of business and society. AI has a great influence over several activities in society, business as well as managing the security of data and information. Hence, there is a need to employ an ethical framework to control activities of AI, which will further increase the benefit of AI and reduce negative impacts. Thestudyhas focused on “virtue ethics”, which refers to a person’s behavior (Hagendorff, 2020). The ethics is concern about practices of habits such as “honesty”, “morality”, and “generosity” (Bbc.co.uk, 2022). The implementation of ethical framework makes AI more “virtuous moral person”, which is useful to guide person as well as technology to resolve ethical complexities. “Consequentialism” is concerned about the consequences of the actions which are conducted by the AI technologies. Application of “utilitarianism” refers to the moral action and its decision making process of AI. Application of deontologyframework in AI system development refers to the development, which emphasis on morality in AI system actions.
It is clear that it provides numerous benefits in working as it has more efficiency and responsiveness to its working (Clarke, 2019). However, the implementation of AI also has some disadvantages. There is a need to analyse the impacts of employing AI in working which will help to identify the benefits as well as disadvantages. AI has to assess the impacts and consequences of its work for increasing its benefits.
Though AI was introduced with an intention of automation in working and processing there is a need to ensure human control over the working of AI (Clarke, 2019). Control of human ova AI-based technologies will enhance the controlling power of AI technologies and also ensure the working of AI.
It is also required to apply safety measures to ensure the safety of human stakeholders which will increase the benefits of and reduce negative impacts (Peters et al. 2020). Safety measures in AI base systems would be effective to ensure the contribution of the systems to human well-being.
Besides safety and well-being measures there is also a need to focus on human rights along with values (Feijóo et al. 2020). Ensuring consistency along with values and human rights will help to avoid negative impacts on individuals as well as organizations. As AI is employed largely in the cyber security field ensuring human value and rights is necessary as an ethical framework.
AI has been employed in sensitive fields such as the protection of personal data and information, risk assessment and management and others (Clarke, 2019). There is a need to enhance transparency in the analysis of data. Ensuring transparency is effective to avoid the use of unauthorised personal data. Transparency in AI systems could also enhance the explanation of its decision-making processes.
As per Clarke (2019), ensuring the quality of work of AI enhances the quality of output and outcome of AI-based systems would enhance productivity and efficiency in business processes as well as in security systems. It would also enhance the accuracy of systems.
It is also required to exhibit resilience on AI systems to mitigate the negative impacts of malfunctioning systems (Clarke, 2019). During the malfunctioning, there are several negative impacts on working processes which harms businesses as well as society. Hence, there is a need to exhibit robustness in AI systems.
PESTLE analysis
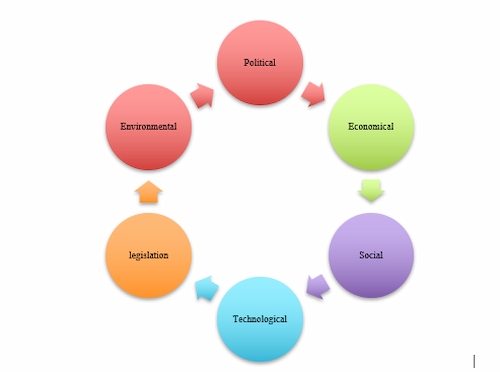
Figure 2: PESTLE Analysis
(Source: Grassi and Vallati, 2021)
Table 1: PESTLE Analysis
Along with all these advantageous sites of Artificial intelligence in business, there are also several barriers faced by businesses due to the use of Artificial intelligence in their business. These are as follows:
First of all, there are issues related to the implication that a large number of technologies in the workplace create difficulties for businesses to manage their cost. Moreover, due to lack of knowledge and skill in the workplace, they need to outsource several pieces of data that make challenges for business and enhance their cost related to the implication of new technologies in business. Furthermore, due to automation in various processes of business, to the collection of data and controlling several machines, proper training needs to be provided for employees that enhance the cost of business (Bunz and Janciute, 2018).
In AI systems due to the uses of several software and programs that need regular up-gradation otherwise, it creates issues related to the Security of data for business. In the case of losing data, it is quite time-consuming and costly for the restoring process. This creates issues in AI implication in business related to systematic up-gradation facilities of software that directly affect the process of business related to data collection and enhance productivity. It can be seen that with emerging new technologies and abundance of data; allows AI methods to improve overall their accuracy (Taddeo et al. 2019).
The application of artificial intelligence has increased to simplify decision making and increase efficiency by improving productivity and accuracy. Algorithmic bias can be defined as an error of algorithms in a system that results in an inappropriate outcome (Raub, 2018). Bias in algorithms of AI refers to a phenomenon where an algorithm considers numerous assumptions in processes of machine learning, which affects the data analysis (Agarwal and Mishra 2021). Fairness in the outcomes of artificial intelligence is very crucial for determining accuracy in work. As per Bellamy et al. (2018), AI bias arises due to inappropriate model applications on big datasets. Biases provide similar treatment to the data set which results in unfair outcomes. For example, if the algorithms of an AI-based recruitment system assume an inappropriate model, it implies ineffective selection of candidates on the basis of gender and qualification. It would reduce the accuracy and efficiency of the system. It also raises the concern of unfair outcomes of data analysis.
According to Bellamy et al. (2018), “AI Fairness 360” or AIF360 has been created to resolve fairness issues in AI systems. The toolkit is open source which has efficiency in identification and understanding of algorithmic biases. The toolkit is also efficient to mitigate biases and increase fairness in theoretical model machine learning (Hufthammer et al. 2020). AIF360 also focuses on the quality of codes.
AI has emerged as an integration of automation algorithms which has efficiency in simplifying complex decision-making processes. With the increasing usages and application of AI, ethical implications are being a major concern. Accountability and transparency are some of the ethical considerations of AI (Dignum, 2019). Accountability and transparency are one of the major concerns as issues arise such as algorithmic bias which affects the fairness of AI systems outcomes. This issue not only affects fairness but also reduces the accuracy of the systems. Hence, there is a need for accountability and transparency of the decision-making process in AI-based systems for ensuring fairness in outcomes (Gevaert et al. 2021). Accountability of AI systems refers to the evidence of governance and defining goals and objectives of systems. Accountability at an organisation's AI-based systems enhances defining roles and explanation of the decision-making processes. Hence, bringing accountability enhances fairness and removes issues related to biases (Bellamy et al. 2018). The issues and challenges in maintaining accountability and transparency are the lack of innovations, infrastructures. Moreover, AI has also been employed in the cyber-security sectors, where maintaining transparency is essential for ensuring the privacy of an individual's data. However, it can be seen that implementing AI in cyber-security can be both beneficial and problematic (Taddeo et al. 2019).
EU GDPR provides guidelines to the users of AI-based systems. GDPR ensures the accuracy and fairness of outcomes of AI-based decision-making processes, which are becoming concerns of AI systems (Taylor, 2019). GDPR has imposed legal requirements for usage of AI which includes fairness to prevent discrimination against individuals, enhances transparency in AI-based systems which enhances meaningful information and explanation of decision-making process and human intervention and control over AI systems to enable control over automated decisions and their processes (BĂLAN, 2019). GDPR also imposes guidelines on the usages of data.
The approach of the EU toward AI is effective to provide benefits to businesses as well as people (Europa.eu, 2022). Policies and strategies of the EU focus on excellence and trustworthy AI. The policies aim to ensure improvements in AI by maintaining safeguards for increasing its efficiency in the public sector by providing safety to society.
OECD principles are aiming to build “trustworthy AI” by ensuring inclusive growth and sustainable development by employing AI, which also enhances the well-being of humans (Oecd.ai, 2022). The principles also focus on increasing human values and increasing fairness in outputs AI technologies. It also emphasizes maintaining transparency in the automated decision-making process (Thiebes et al. 2021). Also, removing robustness in AI systems ensure security and safety. Bring accountability is also a major concern of OECD.
Us policy and strategies on AI aim to improve its efficiency and accuracy by enhancing transparency, accountability and fairness of output of artificial intelligence. However, several States of America have enacted several legislations to regulate guidelines of uses of AI (Ncsl.org, 2022).
The “data protection” law of the UK is a technology-neutral legal framework (Gov.uk, 2018). DPA has no direct guidelines for the usage of AI-based technologies. However, the UK’s GDPR and DPA have focused on automated personal data processing (Ico.org.uk, 2022). These two legal frameworks have provided guidelines for the profiling of information and decision-making through automated devices. Hence, DPA has focused on automated data processing to ensure the safety of data and transparency of data usages.
Governance of AI is crucial for managing the risks of AI. The importance of governance is to utilise the benefits of AI technology. AI technologies increased efficiency as well as delivered quality to the people. However, the autonomy of usages of AI may harm the privacy of data as well as reduce safety measures in operations (Linet al. 2017). The concerns of governing AI arise in the sectors of transport, healthcare and emergency response (Taeihagh, 2021). It is also concerned with several socio-economic factors. The application of AI aims to provide sustainable development. Hence, AI systems are essential for developing perspectives. The main issues with the aspects are complexity in AI and respective risks with smart devices and AI systems, which are increasing with its evaluations. Hence, there is a need for governance mechanisms, particularly for healthcare sectors, managing autonomous weapons (Ulnicane et al. 2021). An effective governance mechanism would be effective to rescue safety concerns.
Advancement in AI technologies increases complexity as well as the availability of data. According to Ulnicane et al. (2021), the ownership of technology is also becoming a major concern as the availability of data to unauthorized owners may lead to misuse of information and breaches of data privacy. Moreover, ownership of technology determines its uses and benefits. Technologies, which are aiming to provide benefits to society, need to be under the ownership and governance of public sectors, whereas AI technologies, which are going to provide benefits to the private sector, need to be under the control of private authorised sectors (Dafoe, 2018). For example, Sectors such as the health sector are needed to take efficient governance for providing effective services and benefits of AI to the society. Similarly is also effective for the private sector as it provides benefits of accurate and efficient data analysis and also provides security to its data.
It has been observed that AI has potential factors to provide value. Hence it can be stated that the implementation of AI is effective to increase future scopes of AI. The section has provided a SWOT analysis of AI to assess future scopes of the technology.
Table 2: SWOT analysis of AI technologies
Analysis of strength weaknesses of AI technologies provides the grounds to improve it for increasing future acceptability of the technology in all economic sectors. Implementation of AI in various public sectors is effective to provide valuable services to the people. Hence, it can be said that the application of AI-based systems is effective to increase productivity as well as efficiency which would increase the value of output and reduce the cost of business operations. Also, as per Wang and Preininger (2019), AI has the potential to provide health services to people. AI is also efficient at resolving complex problems very quickly. Autonomous weapons are also operated by AI for example, “Lethal Autonomous Weapons Systems” (Belfield, 2020). It signifies the future opportunities of AI. However, the analysis has also signified the ethical as well as risk concerns of using AI systems, which news to be addressed by enhancing research and development. Also, there is a need for more innovation for evolving the technology (Canals and Heukamp, 2020).
Conclusion
It can be concluded that AI has a great influence over businesses as well as society. In industry 4.0 plays a key role in business operations. However, the use of AI technology razors some concerns such as accountability, transparency, control of humans and other ethical concerns. Meeting off the ethical concern would increase the accuracy and fairness of the outcome of AI systems. The study has found that there are several legal frameworks that focus on mitigating legal issues of AI systems such as EU GDPR, OECD principles and US policy and others, which can be referred to build an effective legal framework for the usage of AI.
Reference List
Books
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking help from our assignment helper. The use...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking help from our assignment helper. The...View and Download
Introduction Visualization Project (R Tool) Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for...View and Download
Introduction to Cisco Cybersecurity and Network Fundamentals Need cybersecurity assignments like this? Assignment Help...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online assignment services. This report...View and Download
offer valid for limited time only*

