Overcome your academic hurdles with Rapid Assignment Help’s expert and student-friendly Assignment Help services.
Answer:
Nervous system
Respiratory system
Cardiovascular system
Digestive system
Musculoskeletal system
Skeletal system
Answer
Cell
Tissue
Organ
Organ system
Answer: Right Lung, Trachea, Bronchiole and Alveoli
Answer: A passageway through which the air passes from the upper respiratory tract to the bronchi.
Answer: To assist in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and lungs.
Answer: Right Ventricle, Capillaries, Pulmonary vein and Vana Cava
Answer: Responsible for pumping blood into the aorta and to tissues all around the body.
Answer: Transports deoxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart.
Answer: Oesophagus, Small intestine, Anus and Liver
Answer: The storage and breakdown of food/chyme through churning and the production of hydrochloric acid.
Answer: Production of pancreatic juices which contain enzymes that aid in digestion, and it produces several hormones, including insulin.
The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide is the main task of the respiratory system (Wheeldon, 2023). Through inhalation, oxygen is taken in and circulated through the circulatory system to the body's tissues. During exhalation, it simultaneously gets rid of carbon dioxide, a metabolic waste product.
The cardiovascular system, which is made up of the heart and blood arteries, conveys blood that is rich in oxygen from the lungs to the body's cells and returns blood that is heavy in carbon dioxide to the lungs for exhalation (Saghiv et al. 2020). This system guarantees that waste products are removed and that oxygen reaches the cells where energy is produced.
Contrarily, the digestive system is in charge of turning food into nutrients that are absorbed into the bloodstream. Then, for energy, growth, and repair, the circulatory system transfers these nutrients to cells.
These systems work together to sustain living by assuring a constant flow of oxygen, nutrients, and waste elimination. They work in unison to keep the body healthy and functioning effectively, with the cardiovascular system serving as the network of pathways that connect the respiratory and digestive systems (Elbers, 2020). The life and general health of the organism depend on this concerted effort.
(A) The three cubes stand for various sizes and surface area to volume ratios. The surface area-to-volume ratio drops as the cubes get bigger. For effective nutrition exchange, waste elimination, and temperature regulation in big organisms, a high surface area to volume ratio must be maintained. Smaller cells can swiftly exchange materials with their environment because they have a bigger surface area compared to volume than larger cells. Larger cells would have difficulty efficiently transporting necessary molecules and getting rid of waste because of their lower surface area to volume ratio (Roy et al. 2021).
Vast organisms are able to maximise these crucial activities because they have a vast number of microscopic cells, ensuring that each cell can easily acquire nutrients and oxygen as well as efficiently eliminate waste. The survival and development of large and sophisticated organisms are supported by this network of numerous, smaller cells that enable essential functions (Newman, 2023).
(B) Organisms need specialised cells and tissues to thrive since they must carry out a variety of bodily activities as well as deal with a variety of environmental obstacles. By improving efficiency and adapting to certain tasks, specialisation maximises an organism's chances of surviving (von Schmalensee et al. 2023). Specialised tissues and cells carry out a variety of tasks. For example, muscle cells are designed for contraction and movement, whereas nerve cells are customised for the transmission of electrical signals. The body's surfaces are covered and protected by tissues, including epithelial tissue. Utilising resources effectively is another benefit of specialisation. Red blood cells, for example, are specially designed to transport oxygen thanks to their biconcave structure and haemoglobin (Chen et al. 2023).
Answer:
Egg Cell - Sperm cells are designed specifically to fertilise eggs. They move towards the egg using a long, whip-like tail structure called a flagellum (Rahban, 2020). DNA that is packed closely within the head is genetic material that is necessary for fertilisation. The acrosome, a cap-like structure at the head, has enzymes that help the sperm reach the egg by dissolving its defences. The successful union of genetic material during fertilisation is ensured by the streamlined structure's mobility and penetration.
_67a9b714a1afa.png)
Figure 1: Egg cell
Ovum (Egg cell) - The female reproductive cells called ova are created for fertilisation. They are nutrient-rich, spherical, and reasonably sized to feed the growing embryo (Cao et al. 2022). Half of the genetic material needed for the offspring is present in the ovum. The zona pellucida, which is its protective outer layer, is crucial for sperm identification and union. It is the perfect choice for sustaining early embryonic development due to its size and nutrient content.
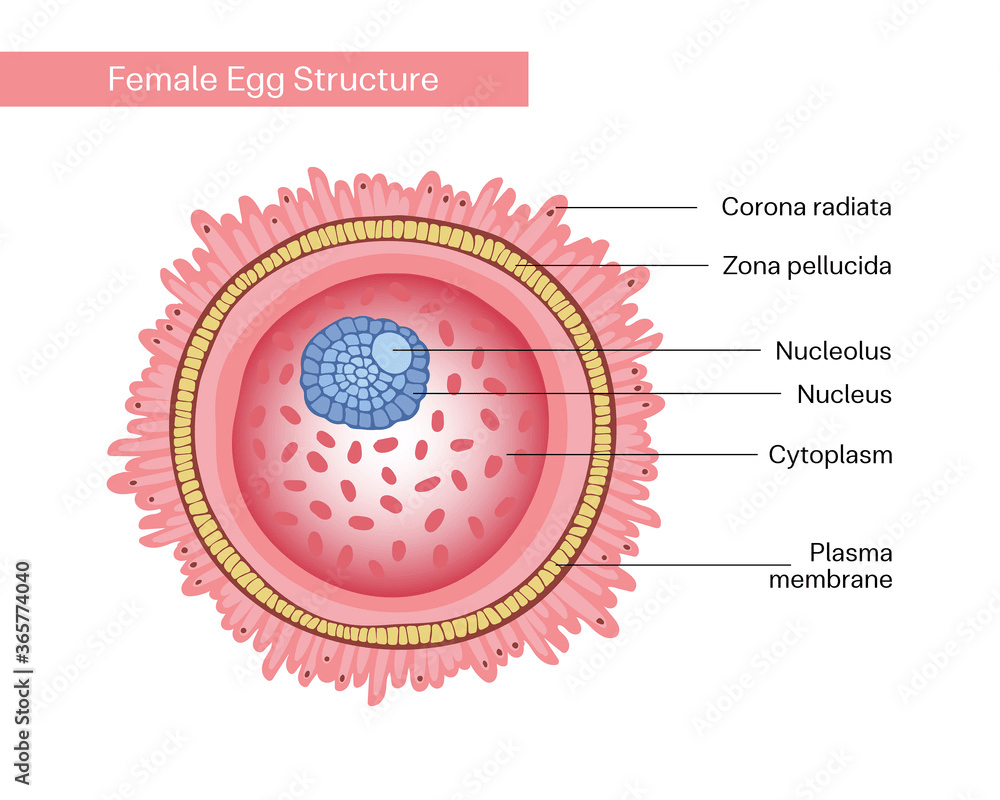
Figure 2: Ovum cell
Neuron (Nerve Cell) - Neurons selectively send electrical signals. They have a long axon that can carry electrical impulses over considerable distances (Drukarch, 2023). Dendrites receive impulses from other neurons. At synapses the connections between neurotransmitters assist in the signal transmission process. Neurons have myelin sheaths, which shield and speed up signal transmission along the axon. Neurons must have a specific shape and structure in order to contribute to the rapid and efficient communication that occurs throughout the nervous system.
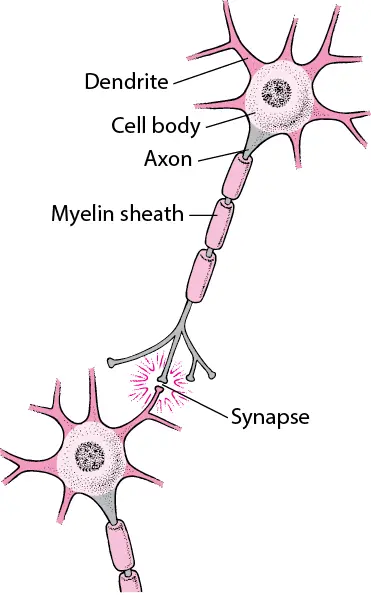
Figure 3: Neuron cell
(Source: msdmanuals.com, 2023)
Ileum's Epithelial Cells - The ileum's epithelial cells are trained specifically for the small intestine's nutrient absorption (Kelly et al. 2022). They have small finger-like projections called microvilli that increase the surface area available for absorption. These cells also include transport proteins that help nutrients traverse the cell membrane more easily. This specialisation facilitates effective nutrition absorption and supports the small intestine's absorptive and digesting processes.
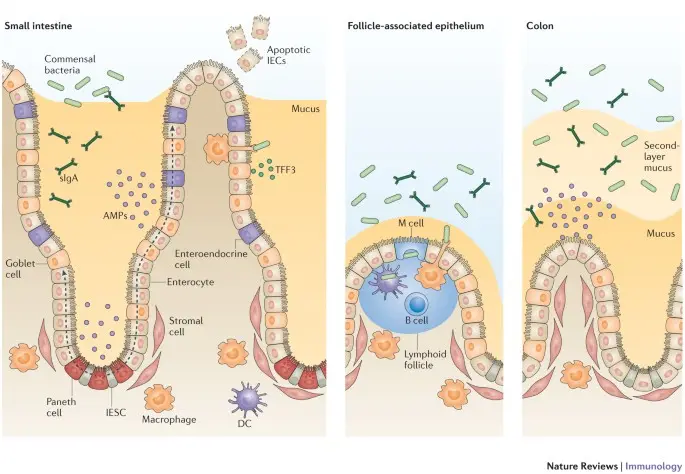
Figure 4: Ileum's Epithelial Cells
|
Tissue Type |
Features of Tissue |
Two Areas Found in the Body |
Function of Tissue in that Part of the Body |
|
A: Epithelial |
Sheets of closely packed cells Apical surface (free surface) |
1. Skin (Epidermis) 2. 2. Lining of digestive tract (intestinal epithelium) |
1. Protection, barrier against pathogens and environmental factors. 2. Absorption, secretion, and selective permeability. |
|
B: Muscular |
Elongated cells capable of contraction Striated appearance (in skeletal and cardiac muscles) |
1. Skeletal muscles 2. 2. Heart (cardiac muscle) |
1. Voluntary movement and locomotion. 2. 2. Pumping blood through the circulatory system (cardiac) and various body movements (skeletal). |
|
C: Connective |
Diverse cell types (e.g., fibroblasts, adipocytes) Extracellular matrix (e.g., collagen fibers) |
1. Bone (Osseous tissue) 2. 2. Blood (as plasma) |
1. Support, protection, and mineral storage. 2. 2. Transport of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products. |
|
D: Nervous |
Neurons (nerve cells) for signal transmission Glial cells for support and protection |
1. Brain (neural tissue) 2. Spinal cord (nerve tissue) |
1. Processing and integration of information, control of body functions. 2. Conduction of electrical signals and coordination of responses. |
Epithelial tissue - Sheets of densely packed cells make up the epithelial tissue that covers different bodily surfaces (Teng, 2021). It creates the skin's epidermis and provides defence against diseases and the elements. It lines the internal surface of the digestive tract, promoting absorption, secretion, and selective permeability. Epithelial cells frequently specialise their apical surface (free surface) to match their tasks.
Muscular Tissue - Long, contractile cells make the elongated structure of muscle tissue. Skeletal muscles are those that are located in muscles connected to bones and facilitate locomotion and voluntary movement (Banerjee, 2023). Smooth muscles control numerous internal organ activities, while cardiac muscles in the heart pump blood through the circulatory system. Striated appearance results from the alignment of contractile units, especially in skeletal and cardiac muscles.
Connective Tissue - Diverse cell types, including adipocytes and fibroblasts, are found in connective tissue (Aprile et al. 2021). These cells are embedded in an extracellular matrix made up of proteins like collagen. Support, defence, and mineral storage are all provided by it in osseous tissue, which includes bone tissue. In its plasma form, blood, a sort of connective tissue, transports nutrients, waste materials, and oxygen throughout the body.
Nervous Tissue - Neurons (nerve cells), which convey electrical signals, and glial cells, which provide support and protection, make up nervous tissue (Halim et al. 2021). It is mostly located in the brain and spinal cord, where it integrates and processes information to regulate different bodily activities (Patton et al. 2023). Axons, dendrites, and the cell body of neurons all play distinct roles in the coordination of actions and the transmission of signals.
Due to their exceptional qualities, which make them a plausible alternative for replacing damaged cells, particularly in regions with restricted regenerative capacity like the brain, stem cells have become a hot topic in the last two decades. We must delve into the crucial characteristics that differentiate stem cells from specialised cells in order to fully grasp their potential. The ability of stem cells to develop into distinct cell types is known as their potency (Tomokiyo, Wada and Maeda, 2019). Totipotent stem cells have the extraordinary ability to develop into any type of human cell, including extraembryonic and embryonic cells. One illustration is the zygote, which is created when an egg and sperm combine and can grow into a full organism.
All three germ layers can be formed from pluripotent stem cells, but they cannot develop into extraembryonic tissues. An illustration would be embryonic stem cells (ESCs), which can differentiate into a variety of cell types but not extraembryonic structures (Poliwoda et al. 2022). Although more limited in their ability to differentiate, multipotent stem cells can nevertheless produce a variety of specialised cells. For instance, hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow can produce blood cells including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. In contrast, specialised cells, such as neurons, cardiac muscle cells, or hepatocytes, are terminally differentiated and carry out particular tasks inside tissues or organs. Unlike stem cells, which still have this capacity for regeneration, they are no longer able to develop into other types of cells.
There are multiple steps in the stem cell-based tissue engineering process:
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
Cell acquisition: A variety of sources can be used to obtain stem cells. While induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are reprogrammed from adult cells, embryonic stem cells are produced from embryos (Ray et al. 2021). In tissues like bone marrow, adipose tissue, or cord blood, adult stem cells can be detected. Through biopsy or other minimally invasive methods, these cells are carefully collected.
Cell Nurturing: After being acquired, stem cells are cultivated and raised in a sterile setting. In order to maintain the right conditions for the cells to multiply and differentiate as required, nurturing is necessary. To direct the cells towards the chosen differentiation path, growth factors, hormones, and certain culture media are utilised (O'Neill et al. 2021).
Directed Differentiation: Stem cells are stimulated to become the particular cell types needed for the target tissue or organ (Fu et al. 2019). By adjusting growth factors, signalling molecules, and environmental cues, stem cells can be guided along the correct developmental pathways.
Formation of Tissues or Organs: Differentiated stem cells are then put together to form tissues or organs that function. Differentiated neuronal cells in neural tissue, for instance, may be arranged into a 3D pattern that resembles the organisation of the brain. Complex structures can be made using a variety of methods, such as tissue engineering and 3D bioprinting (Feng et al. 2021).
In conclusion, stem cells present a promising way to replace missing or injured body parts, especially in regions like the brain where neuron regeneration is constrained. Obtaining the right stem cell source, fostering and directing their development, and finally producing functioning tissues or organs for therapeutic uses are the stages of tissue engineering. While stem cell research is still developing, it has the potential to completely change regenerative medicine and enhance the lives of people with a variety of degenerative diseases.
References
Task 1 Achieve academic excellence with Rapid Assignment Help, offering expertly written and affordable Assignment Help. Answer...View and Download
QUESTION: 4 Get timely, well-researched help with your Online Assignment Help, ensuring you stay on top of your...View and Download
QUESTION 1 Enhance your academic performance with Online Assignment Help. Get expert guidance, well-researched content, and...View and Download
CACHE Level 3 Diploma in Early Years – Unit 1 This section provides complete solved work for CACHE Level 3 Diploma in...View and Download
Part 1: Understanding NIST, Wireshark, and Ransomware Threats Cyber threats are evolving, making online Assignment Help Services...View and Download
QUESTIONS Enhance your knowledge and skills with Assignment Help Online Experts, ensuring high-quality academic support for...View and Download
