Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment Help services.
Diversifying operations into other host countries has become an integral success factor for ventures in today’s competitive business environment. It is undeniable that organisations are striving to expand their operations into foreign markets, which in turn, fortify their competitive edge in global market. In this context, significance of HRM comes forth, which assists to streamline MNCs’ diversified operations and activities across borders. Human resource management is considered as a backbone of a firm regarding the fact that employees are building blocks of international companies.
The study will focus on key essentials related to HRM during situations where multinational companies seek to diversify operations into other host settings. An emphasis is provided on functions of HRM during MNCs’ diversification of operations into foreign territories alongside their role. These will also be backed up with relevant theories and examples, which assist to derive a profound conclusion in this study.
Human resource management (HRM) is generally a strategic function of any multinational company that is highly concerned with recruitment of staff, training, as well as development for growth of the organisational productivity. HRM for multinational companies is all about the development of knowledge, skills along with the management of skills, creativities, and talent for maintaining a skilled staff base. Maintaining sustainable strategy by HRM for the growth of an organisation is an important aspect especially for those MNCs. The sustainable strategy of HRM mainly focuses on maintaining a sustainable system in the workplace along with consideration of economic, social, as well as environmental aspects (Macke and Genari, 2019).
HRM is an important concept for MNCs as it helps in planning for maintaining functionalities of any MNC without any barrier. HRM has the role in planning for business, controlling, organisation of the activities of MNCs, proper utilisation of workforce along with accurate staffing.
Designing a job and analysing the effectiveness are important roles of an HRM department member to make the plan successful for achieving the business goal. However, management has a role in controlling the HRM functionalities within any MNC. The HRM department needs to secure strong support from top-level management for boosting the empowerment of employees by providing contentious training to improve productivity (Chams and García-Blandón, 2019). Different multinational companies use their HRM department to maintain the skilled staff base for maintaining effective productivity for maintaining a competitive position in the market. An example of the HRM strategy of Unilever indicates three important strategies for future growth such as helping people to become future-fit, employment flexibility and developing skills for young people (Unilever.com, 2022).
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
Figure 1: Tasks of HRM
(Source: Macke and Genari, 2019, Chams and García-Blandón, 2019)
Planning and providing training to staff are essential aspects of the HRM department in MNC to make the employee accustomed to the working environment of MNC. Training is termed as a systematic strategy for the development of the employee skill, abilities, as well as knowledge for the improvement of organisational effectiveness (Fletcher et al. 2018). Strategies of HRM is the final one in providing benefits, compensation, along with maintaining communication strategy with employees to achieve a collaborative work environment. Further, HRM is the department in an MNC that helps in selection along with maintaining a good relationship with stakeholders who are beneficial for an MNC.
HRM implements different health as well as safety regulations within MNCs to safeguard employees from risk. Another example is HSBC in which the HRM strategy is influential in recruitment, effective reward management and talent management for the development of new opportunities (About.hsbc.co.uk, 2022). However, some challenges are associated with the HRM department especially for handling functions of MNCs. Diversity management is a serious challenge for HRM in a MNCs different staff work within an MNC. Creating job opportunities in the future is another challenge that the HRM department needs to handle for the improvement of a business. Maintaining networking especially during this pandemic has provided a challenging task for HRM of MNCs. Relationship management with reducing conflict between staff is a challenge that HRM needs to deal with within MNCs.
Human resource management in a multinational company is accountable to maintain a wide variety of activities, starting from global staffing to international labour mobility and various others. Recruitment and selection are regarded as fundamental responsibilities of HRM, which are extended to employee retention, accelerating innovation with regard to individual performance, and various others integrated into international businesses (Cooke, 2018). However, since MNCs are continually diversifying operations to expand businesses in other host countries, HRM is demanded to work in a wider spectrum, which is accompanied by a number of challenges. These issues of HRM during companies’ expansion into foreign territories can not only drain organisational resources but also hinder organisational operations drastically.
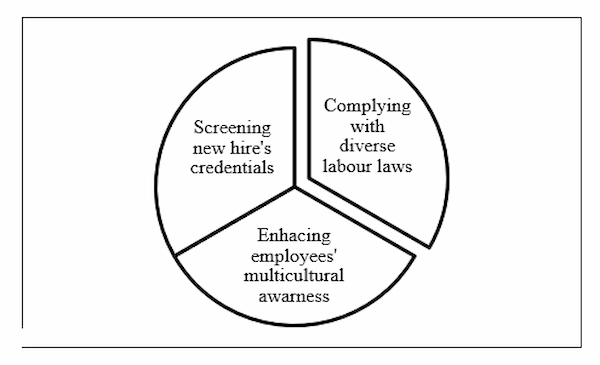
Figure 2: Challenges witnessed by HRM in MNCs during diverse operations in foreign territories
Under the concept that a skilled and critical workforce is intrinsic during diversified operations of multinational companies into other host countries, cross-border recruitment is facilitated by HRM to acquire talents. Fortifying authenticity of employees’ academic credentials and other essentials can be often challenging, as companies initiate to enter into other nations, which indeed have distinct cultures (Kontzinos et al. 2020). Hence, additional efforts are needed by HRM to refrain from wrong hires, which can disrupt operations as well as financial resources of MNCs.
According to Mahmoud et al. (2019), expenditure of any wrong hire is an average of $15,000, which is a moderate expense of losing a good hire. Hence, HRM in MNCs often witnesses challenges of time-consuming and incurred costs associated with cross-border recruitment. For instance, in response to these issues, one of the leading multinational enterprises in UK, Unilever has integrated AI to alleviate time consumption and additional costs in human recruitment (Theguardian.com, 2019). Thus, HRM needs to incorporate efforts to ensure a skilled workforce, which can retain MNCs’ diversified operations in other host countries.
Multinational companies are expanding their businesses into distinct host countries to retain their competitive edge in global market. In this regard, without critical talents, MNEs will not be able to flourish their sustainability in a contemporary business environment. Glazyrina (2020) propounded that one of the concerning constraints witnessed by HR departments during MNCs’ expansion into other host countries is compliance with labour regulations, laws, and norms. It further emphasised that any changes in labour laws of diverse countries demand international HR practitioners to alter company policies to be in line with established regulations in host country. Since labour laws and regulations vary dramatically from one country to another, HR professionals in MNCs need to be well aware of this continually and adjust accordingly, which can be highly challenging.
Compliance with labour laws includes wage systems, working hours in host countries, and various others while MNCs seek to diverse operations into international territories. A recent BBC report exhibits that UK supermarket chains, such as Tesco, Sainsbury, and Marks and Spencer are facing criticisms due to their failure to comply with Indian labour law, as Indian workforce supply volumes into these MNCs (Bbc.com, 2020). It is noticed these UK supermarket chains promote overtime, which clearly violates the Indian labour law of India’s Factories Act suggesting work cannot be exceeded 48 hours a week, and hence, exploits Indian workforce. It indeed creates immense pressure on HRM, which further disrupts international operations in other host countries.
Employees’ works in other host countries become highly prevalent due to MNCs’ diversified operations in various territories. It demands human resource management to integrate training, which is intended to enhance individuals’ multicultural awareness. According to Jawad (2020), one of the biggest challenges witnessed by international human resource management (IHRM) in multinational enterprises, is maintaining expatriates to ensure that diverse cultural activities of host countries align with MNCs’ strategies. It influences HRM to put efforts as well as organisational resources into extensive training and development, which is to assure a higher sensitivity and awareness towards cultures of other host countries. Here, Cooke et al. (2019) argued that maintaining a diverse culture in other host countries can be challenging for IHRM in MNCs, which are expanding operations in other host nations. It further emphasised that higher payment for expatriates in comparison with local nationalities can raise internal issues, such as discrimination, inequalities, formation of subgroups among workers, and others.
Regarding these high ranges of cultural issues prevailing in multinational companies expanding their operations in other host nations, IHRM is forced to invest largely in training and development. One of the leading financial institutions in UK, HSBC incorporates Cultural Exchange Program considering its diverse operations in China in response to the fact that cultural differences persist between Chinese culture and Western attributes (Hsbc.com, 2022). Hence, successful HRM of this bank fosters a cohesive diverse culture following HSBC’s operations in 64 other host nations.
Importance of human resource management comes into play more exponentially when MNEs expand their operations into other host countries. Strategic HRM helps in organising essential expatriate systems and policies, along with maintaining effective staffing frameworks across borders (Edwards et al. 2019). It further illustrated that HRM plays a key role in MNCs operations and expansions in foreign territories by ensuring a favourable convergence of domestic employees from other host nations, third-party nationals, expatriates from their home country. Hence, it would not be wrong to mention that without human resource management and its effective functions, multinational enterprises will not be able to facilitate successful operations in global market.
In this regard, international HRM becomes more important as well as complex for MNCs as compared to domestic HRM. Farndale et al. (2019) reported that domestic HRM is responsible to manage workers in a single country, whereas IHRM is involved with managing workforce from host country, home country, and a third country, an essential factor for MNEs. Hence, starting from cultural differences to ensuring productivity of workers, maintaining effective employee relations, retaining workers, and others are to be fostered by HR department. According to Sharma and Matta (2018), effective IHRM policies and practices have become success factors for multinational companies to retain workers, as an increase in expansion of MNCs enables employees from distinct cultures to work together. Training and development, employee retention along with IHRM practices are key factors, which determine organisational sustainability in other host countries.
A number of international practices are adopted by HRM in multinational companies, which not only assist to motivate diverse workers but also help to retain them. It is evident that MNCs’ diverse operations in other host countries incur costs and are time-consuming, during which high employee turnover rates can be challenging for organisations. Akunda et al. (2018) reported that retention and talent management are integral aspects of HRM to foster sustainable business strategies of MNCs. Thus, importance of human resource management in MNCs is undeniable considering its wide range of practices and roles, which strengthen international firms’ diverse operations while seeking expansion in other host countries. A number of UK companies are facilitating operations into other foreign territories, which are intended to derive their advantageous edge in a competitive business environment.
Human resource professionals operating in multinational companies play significant roles, as they can maintain a productive work environment. It is conducted by HR’s efforts to fortify an internationally diverse employee pool, which has knowledge and skills to work together. However, maintaining a cohesive work environment is definitely not easy, and requires a wide range of functions. These are briefed down in this section of the study.
International recruitment and selection
International recruitment is often perceived to be global staffing, which is conducted to meet requirements of multinational companies while seeking expansion or diverse operations in other host nations. According to Hamza et al. (2021), conventional recruitment process involves clarifying positions to be filled, updating job descriptions as well as specifications, determining probable sources, and communicating through interviews. Nevertheless, international recruitment and selection derive a handful of additional activities, starting from relocation on selection to extensive communication to make new hires aware of MNCs’ culture and other information. Klietsova and Mykhailova (2021) opined that local culture and regulations have innate influences on recruitment in MNCs during their expansions in foreign territories. It further emphasised that international HRM needs to comply with existing labour laws during recruitment, which is different across borders, and accordingly. Hence, wage systems, working hours, and others are to be communicated in an in-depth manner before selecting right candidates.
Moreover, international recruitment and selection demand extensive efforts of screening, which is time-consuming. This is where importance of Unilever’s AI-enhanced recruiting comes forward, as this multinational consumer goods brand recruits 30,000 people annually by processing 1.8 million applications from 190 host nations (Forbes.com, 2018). Another leading pharmaceutical company, GlaxoSmithKline’s IHRM strives to maintain employment rights in US by complying with Federal Law, which fosters its competitiveness in this host country (Us.gsk.com, 2022). Thus, HRM needs to provide additional efforts during international recruitment and selection in MNCs.
Facilitating global collaboration
Since companies are becoming more global with expansion in other foreign territories, HRM professionals are inclining more towards profitability, competitive advantages, and economic sustainability during stringent financial times. Nevertheless, in wake of managing a diverse workforce, which is an integral part of MNCs’ work environment, human resource practitioners feel pressure to foster global collaborations to stimulate organisational performance. Przytu?a et al. (2020) propounded that in response to a surge of a global pandemic, virtual collaboration can be driven by strategic HRM through extensive communication. A supportive argument is noticed that continual changes in international markets have brought uncertainty among international workers, which is retorted with promotion of collaboration by international HRM strategies (Caligiuri et al. 2020). It not only hinders their motivation but also individual performances resulting in disruptions of organisational productivity in host nations.
In this regard, HRM of leading multinational companies involves strategies to ensure collaboration within a diverse workforce. For example, Google celebrates April fool’s Day every year, which allows employees from different cultures to play games, such as ping-pong and volleyball during breaks (Tews et al. 2019). Such HRM strategies not only boost employees to contribute their potential but also foster their collaboration to ensure cohesiveness and enhanced productivity to work for a shared goal.
Providing ongoing training and development
Apart from fundamental functions, such as cross-border recruitment by human resource management in MNCs during their expansion in other host territories, ensuring their skills and knowledge that are in line with organisational goals is to be determined. In this regard, HRM plays a key role in maintaining an internationally diverse pool of workers, which is intended to create a productive environment, and hence, it is conducted by training (Khan and Abdullah, 2019). Extensive training and development shape necessary essentials of an employee to increase competencies and skills, and thus, accelerate their productivity, which is essential during MNCs’ diverse operations in other host countries.
Figure 3: Influence of training and development on workers’ productivity
(Khan and Abdullah, 2019)
Added advantages of training and development facilitated by international human resource management, such as employee motivation, as well as employee retention, are noticed in MNCs in today’s business environment. For instance, Burberry is one of the leading UK-based luxury multinational corporations, which dominates the fashion industry across borders. Considering its diverse operations in foreign markets, HRM of Burberry has launched a three-stage diverse initiative with regard to training for its employees from diverse cultures (Vogue.co.uk, 2019). Such training facilities are intended to make cross-cultural employees be acquainted with this MNC’s culture along with enhancing their skills and proficiency. Considering its diverse operations in multiple host territories, HRM of GlaxoSmithKline strives to appoint diverse talents, which are moulded by a wide number of training and development facilities, such as the Accelerating Differences - Ethnic Diversity Programme (Gsk.com, 2022). Hence, such training programs allow employees to enhance their awareness concerning multiculturalism, leading to sustainable organisational performance in foreign countries.
Rewards and recognition for motivation
Rewards and recognitions are perceived as key essentials to ensure employees’ motivation and their intention to stay in MNCs. Hence, apart from maintaining substantial pay and compensation to workers, human resource management in multinational enterprises integrate rewards and recognitions. According to Hussain et al. (2019), implementation of rewards and recognitions not only enhances employee engagement but also accelerates their performance, which is important for MNCs while operating in other host nations. In addition, rewards, and recognition enable employees to experience a sense of belongingness, and hence, stimulate them to deliver their potentials.
Added benefits of such HR practices of accreditation and rewards alleviate possibilities of absenteeism, lower productivity, and high turnover, which can fortify MNCs’ sustainability in foreign markets. Regarding the fact that employees fuel sustainability and competitiveness of businesses, a renowned apparel brand, Marks and Spencer (M&S) rewards its employees with M&S Corporate Gifts, which is intended to nurture employee relations and retain staff in global market (Marksandspencerforbusiness.com, 2022). This famed British retailer has been diversifying its operations in multiple foreign territories, and therefore, its global staffing reinforces M&S’s operations across borders. This is where HRM plays a crucial part in ensuring a flexible environment for employees, which can result in their retention.
This study has explored importance and roles with regard to functions of human resource management in MNCs during their diverse operations in other host territories. In this context, application of two pertinent HRM models is briefed down in this section of the study to grasp effectiveness of HRM in maintaining a diverse workforce, which can contribute to organisational goals. It is intended to strengthen the concept that HRM is backbone of MNCs in today’s competitive global market.
Standard Causal Model of HRM
A causal model of HRM indicates that strategic HR activities and practices, which are in line with organisational strategies, can result in enhanced business performance. HR practices, according to this model, are extracted from overall company strategies, which regard areas, such as recruiting, training, appraising, and compensating. Nevertheless, Collings et al. (2019) argued that to maintain pivotal positions of MNCs in global market, HR practices and strategies are to be aligned with local contexts. Hence, HRM needs to give keen attention to dimensions, such as national wage systems, working hours, and other essentials of host nations.
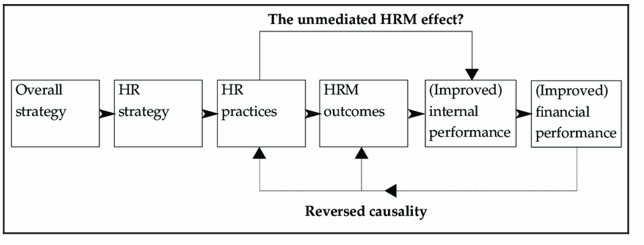
Figure 4: Causal model determining a link between HRM and performance
(Source: Matsumoto, 2019)
This model further illustrates that effective HRM strategies lead to certain outcomes, such as high engagement, commitment, and others, which eventually, result in enhanced internal performances (Matsumoto, 2019). Hence, it is indeed that improved performance, such as innovation, higher productivity, and more accelerate financial performance of MNCs in other host countries. It is noticed that a wide number of companies in UK have been driving their diverse operations across borders, and thus, implementation of this model by HRM can strengthen their competitiveness and sustainability in foreign markets.
Eight Box Model of HRM
Contemporary business environment has been witnessing a number of changes, which make uncertainties and other risks prevalent for MNCs while expanding into international territories. Here, Mala (2020) illustrated that 8 Box Model by Paul Boselie exhibits that a handful of internal and external factors, such as legislation, macroeconomics, and others can shape human resources. For instance, differences and variances in labour laws with respect to working hours, wages, and others prevail in diverse nations.
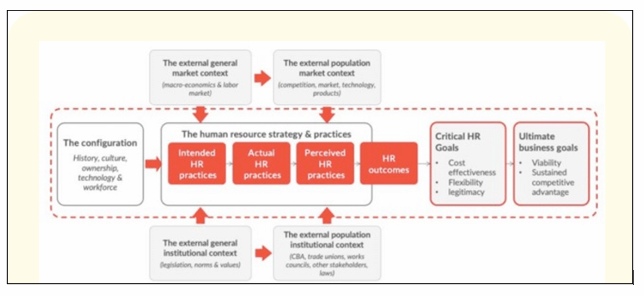
Figure 5: 8 Box Model of HRM
(Source: Mala, 2020)
Hence, 8 Box Model of HRM consolidated HRM practices into three parts, which are intended HR practices, actual HR practices, and perceived HR practices that lead to ultimate HR outcomes. Eventually, critical HR goals and ultimate business goals in MNCs determine organisational sustainability in other host countries (Mendy et al. 2020). Following issues faced by UK supermarket chains, such as Tesco, M&S, and Sainsbury due to inadequate compliance with labour laws while diversifying operations in host countries, this HRM model can be effective to retain their sustainability. Hence, application of this HRM model can make internationalisation easy for MNCs while seeking to diversify operations in foreign nations.7. Conclusion
From this above study, it can be concluded that HRM is a driving factor in MNCs to maintain their competitiveness and sustainability while expanding into other host countries. It is noticed that international HRM is far more complex as compared to domestic HRM, as MNCs are associated with integration of employees from their home country as well as host nations. Considering the high growth of MNCs, HRM is found to play core functions to maintain a workforce that can contribute to organisational goals in cross-border settings. In addition, the study has delved deep into challenges witnessed by IHRM, which are backed up with examples to grasp their concerns. Besides, a couple of relevant theories are also incorporated in this study, which is intended to exhibit feasibility of these for HR professionals in MNCs while taking international initiatives.
Reference list
Journals
Websites
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction: How Business Can Benefit From Sustainable Business Practices Get free samples written by our Top-Notch...View and Download
Task 1 The training and CPD sample demonstrates how effective training can enhance staff skills. For assignments on hospitality...View and Download
Introduction Get Free Online Assignment Samples from UK's Best Assignment Helper Experts to boost your academic...View and Download
Introduction :Working with Individual Learners Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking assignment help uk from Rapid...View and Download
Copyright 2025 @ Rapid Assignment Help Services
offer valid for limited time only*

