Achieve more with less effort through Rapid Assignment Help’s efficient and results-driven Assignment Help services.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
In the UK, the tax system for companies is intricate and multidimensional, reflecting economic policies, historical practices, and the desire to strike a balance between income production and justice. Let's examine critically by looking at the rationale for the tax disparities amongst sole proprietors and incorporating firms, the distinction between capital gains and income taxes, and the difficulties and solutions to simplify the tax system.
The legal form of enterprises is one of the main causes of tax differences. Some traders are subject to separate taxes and are subject to limitless liability, which puts their personal assets at risk. Limited liability for business organizations keeps personal and company assets apart and results in differing tax implications for them (O’Brien and Pike, 2019).
Since the concept of income tax's inception, the UK's tax code has changed, with distinct tax treatment for businesses and individual proprietors. The tax system is still influenced by this historical history. Fairness and accessibility are two further factors that determine the difference between companies and single proprietors (Maffini et al. 2019). Since corporations have minimal accountability, it is appropriate to tax their earnings at higher rates.
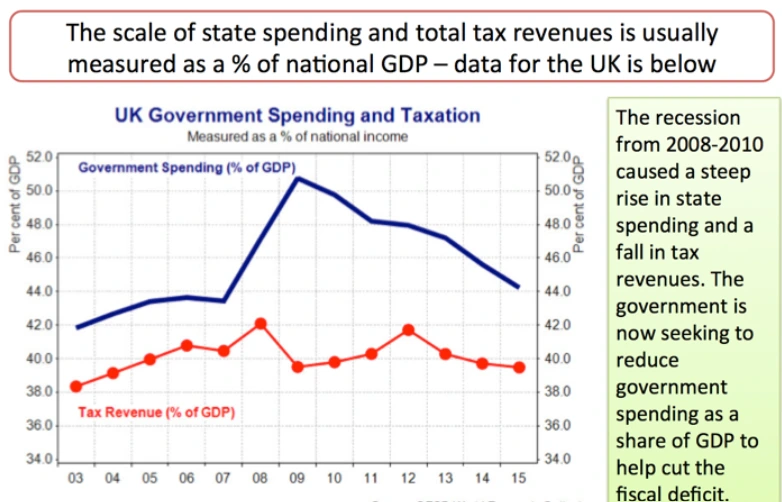
Capital gains taxes are intended to foster investment, entrepreneurship, and economic progress, whereas taxation on earnings is mostly employed to support public services and reduce income disparity.
Tax computations are made simpler by combining income and capital gains. Politicians may find it difficult to prevent tax-related preparation and avoidance, nevertheless, as a result of this. Taxing both earnings and investment gains accomplishes distinct economic goals. The purpose of taxing income is to redistribute wealth and raise money (Best and Kleven, 2018). Investment gains taxes offer favoured rates on profits from investments in property, which stimulate investment and entrepreneurs.
The intricate tax structure in the United Kingdom presents prospects for fraudulent activity and evasion of taxes. Legislators have worked to improve tax enforcement, enact anti-avoidance measurements, and streamline the tax law (Bournakis and Mallick, 2018). The UK must modify its tax structure to handle the problems posed by the growth of digital firms and internationalized markets, particularly with regard to the taxation of international companies.
Achieving tax equity is still a difficult task and it's difficult to strike a balance between making sure all companies pay the appropriate amount of taxes and encouraging entrepreneurial and economic growth. As per the narration of Carattini et al. (2019), legislators frequently alter tax laws to reflect shifts in the economy and in how businesses operate. One example of this is the implementation of Making Tax Digital (MTD), which would streamline the process of paying taxes.
Struggling to grasp supply and demand curves or economic equilibrium? Our economics assignment help simplifies these concepts, providing clear explanations and well-researched solutions.
The idea of equality is reflected in UK tax policies, which aim to impose a heavier tax burden on individuals and firms with higher earnings or profits. This is achieved principally through the use of progressive income tax rates. As per the narration and explanation of Gavazza et al. (2019), the tax system seeks to manage complexity and assure cooperation while reflecting core ideals and taking into account the current economic and political situation of the United Kingdom.
The Entrepreneur's Relief and Investors' Relief favourable capital gains tax rates are designed to incentivize participation and support entrepreneurial activity. The government's determination to combat tax evasion and avoidance is evidenced by the General Anti-Abuse Rule (GAAR) and the Diverted Profits Tax (DPT).
In tax policy, the subject of whether various business kinds should receive different tax reductions is a complicated and hotly contested topic. Differential tax concessions' suitability ultimately depends on a number of variables, such as societal ideals, ease of administration, justice, and economic objectives. Some considerations are listed below:
Various company models fulfil distinct economic functions. Achieving certain policy goals might be facilitated by offering tailored tax breaks. For instance, offering tax breaks to new and small companies can encourage economic expansion and entrepreneurship.
Equity problems can be addressed by tax concessions. In order to level the playing field and assist those in need, concessions for low-income companies or sectors suffering financial difficulties, for example, might be considered.
Whenever too many concessions are introduced, the tax system may become too complicated. Organizational difficulties, tax evasion, and higher compliance costs for companies and tax authorities are frequently caused by complexity.
Differentiating tax breaks might raise issues with horizontal equality, the theory that people or companies in comparable economic circumstances ought to pay similar taxes. Giving preference to some companies might be seen as unjust to others.
Concessions have the potential to lower governmental income, which might restrict the amount of money available for the construction of public facilities and amenities.
In actuality, finding a balance is frequently required when deciding which kinds of firms should receive distinct tax breaks. The precise budgetary, social, and economic goals must be taken into account by policymakers, as well as any possible negative effects of making such compromises. Streamlining the tax law, closing loopholes, and making sure tax breaks are clear, well-targeted, and routinely adjusted to reflect shifting financial circumstances are a few choices (Alesina et al. 2019). In the end, the suitability of various tax breaks is determined by the broader context of tax policy, the government's particular objectives, and the necessity of fostering economic growth, equity, and transparency while guaranteeing sufficient funding for the delivery of public services and goods.
Due to its many exclusions, subsidies, and incentives, which may make administrative and compliance difficult, the UK tax system might need some clarification and simplicity. Since financial and social gaps still exist in the UK, achieving equality and justice in the tax system will be an ongoing struggle. Sustainability should be promoted by the tax system as environmental concerns gain importance. A review of the tax code is necessary due to the emergence of the internet-based economy and the difficulties in imposing taxes on international companies. In order to ensure that the tax system is in line with the nation's changing economic and social objectives, it needs to be regularly reviewed and evaluated. Administrative effectiveness and the capacity to stop tax fraud and minimization are crucial.
Reduce the amount of exclusions, allowances, and incentives in the tax system to make it simpler. In order to reduce the cost of compliance for both people and corporations, strive for a tax system that is more clear-cut and straightforward. In order to cut down on the expenses associated with compliance for both people and businesses; strive towards a simpler and more transparent tax system. Assess the tax system's progressiveness and take changes into account to make sure that people with greater wealth and salaries pay their fair amount and if it is thought suitable, investigate possibilities for reducing wealth disparity, such as a wealth tax. In order to foster creativity and competitiveness, governments will keep offering specific tax advantages to companies, such as R&D tax credits. Work together with foreign partners and modify tax legislation to adequately handle the issues associated with taxing internet services and multinational businesses.
Reference list
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Understanding Key Legal Concepts and Historical Developments Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking help from our assignment...View and Download
Introduction: A Study of Transformational and Authentic Theories from Peter Cowgill’s Leadership Get free samples written...View and Download
INTRODUCTION Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction: Psychology Postal Assignment: Depression Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking...View and Download
Copyright 2025 @ Rapid Assignment Help Services
offer valid for limited time only*

