Health inequalities are one of the major problems of every country. Every country has faced major problems to mitigate these problems. However, Health inequalities are also causing many poor and underprivileged people in the world. Many people die every day because of high Health inequalities in the world. The world is becoming more unequal every day in terms of access to health benefits, wealth, and income and also in terms of the life expectancy of people in the world. Along with that Health inequalities are also affecting the lifespan of many poor people in the world as the GDP of various countries has seen rapid growth in recent years. However, the economic condition of many poor people is the same in various countries that are increasing Health inequalities in the world. As stated by Bambra (2021), social inequalities in health and income, race, and deprivation of neighbourhood and seen significant growth.
Hence in India Health inequalities in social-economic is evident as many people in India are facing problems in getting basic treatment processes for a disease. Hence this paper has focused on the situation of diabetes patients in the country. Diabetes is a severe disease that requires a long-term treatment process that takes expenditure of money. However many people in India are not able to follow the remedy process of diabetes because of lack of money. On that account, this report has shed light on Health inequalities in India. Besides that, this paper has focused on providing various PHS ( public health strategies) that can help to reduce Health inequalities in the country. Moreover, this paper has focused on poverty and low numbers of medical staff in the country.
Health inequalities are common across parts of the world as many people face problems getting a good treatment process that impacts their lives and health conditions. Moreover, it also defines " the systematic differences in the health of people occupying unequal positions in society". Moreover, it can also be found in diverse aspects of society such as income, status of economic, caste, geography, and background. As per their view of the Who.int (2018), in the world over 1 billion people live in slum conditions. Hence health inequalities are major problems of the world that impact many patients' lives in the world as they do not have enough economic stability. Along with that racism in the health sector of the world is also a major problem that also increases health com in the world. As opined by Hamed et al. (2022) racism is one of the major barriers that created problems for the healthcare sector to achieve equality in the healthcare system.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
However, South Asian countries have seen significant growth in the social and healthcare sectors after the post-colonial period. However many areas of South Asia are underdeveloped in terms of the health sector which has created major health inequalities problems in that region. Moreover, the healthcare sector of South Asia has lower overall life expectancy and also increased child mortality, and discrimination of gender that has impacted the health condition of many people in that area. As stated by Sathi et al. (2022), in South Asia low birth weight and health-related education have evident inequalities. India is one of the fastest growing economies and developing countries however the country has also faced major health inequalities in countries that have increased mortality. As stated by Salvi et al. (2018), India has a population of 18% of the world but the country has over 32% of global DALYschronic respiratory health issues.
Along with that diabetes is one of the most common diseases that has created diverse challenges for the country and also increased their health inequalities in the country. According to Indianexpress.com (2023), in India, over 101 million people have diabetes issues. Besides that in India over 136 are in the pre-diabetes stages as per a recent study of ICMR (Indianexpress.com, 2023). Thus diabetes is one major disease in the country that created major problems for India even though India has developed their diabetes treatment process in recent years that has helped many people to get out of diabetes problems in the country. As per the view of Statista.com (2023), in India, over 74 million people will be diagnosed with diabetes in 2021. On that account diabetes is a major problem for various treatment processes and has increased health inequalities in the country. Inequality in India's healthcare sector is one of the major problems of the country.
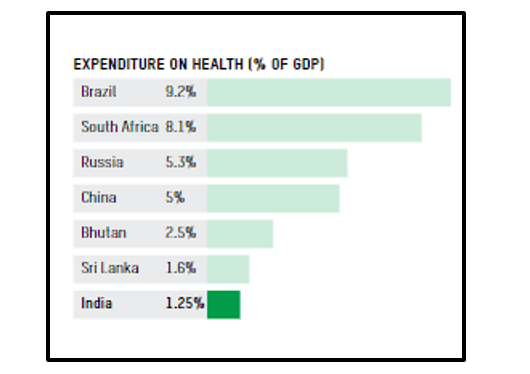
Figure 1: expenditure on the health care system of India by its GDP percentage
(Source : Ruralindiaonline.org, 2022)
As opined by Ruralindiaonline.org (2022), in India only 1.25% of their GDP is spent on healthcare compared to that of 9.2% in Brazil and 5 % in China. Hence the above picture shows inequality in Indian healthcare spending. According to Ruralindiaonline.org (2022), in India, there is only 1 government-employed doctor of allopathic for over 10,189 people. Along with that, Indian states run a hospital for over 90,343 people (Ruralindiaonline.org, 2022). On that account, these stats show huge health inequities in India that exist in the healthcare sector of the country.
Health inequalities are caused by diverse economic, social, and political issues; however, some inequalities in health care are also caused by unequal allocation of primary amenities of society. Along with that poor structure of health is also one of the major aspects of health inequalities besides that inequalities in the income of individuals are also one of the causes of health inequalities. As stated by Schenkman and Bousquat (2021), inequality in income is a major reason that accuses equitable access to education for the health of a person. Along with ppp in economic-socio also leads to health inequalities in the health sector. Hence there are various reasons behind health inequalities such as poor access to healthcare, income and wealth distribution education, age, and genetics. If a person lives below the poverty line then they will get a different environment for healthcare and people who have strong economic stability have more advantage to get proper medical facilities.
Moreover, poor people also have limited income and also little access to primary health centers and they are not financially capable of acquiring proper education and food. Hence it results in a poor person having to suffer all of their life which can lead to a lower rate of life expectancy and poor quality of healthcare care.
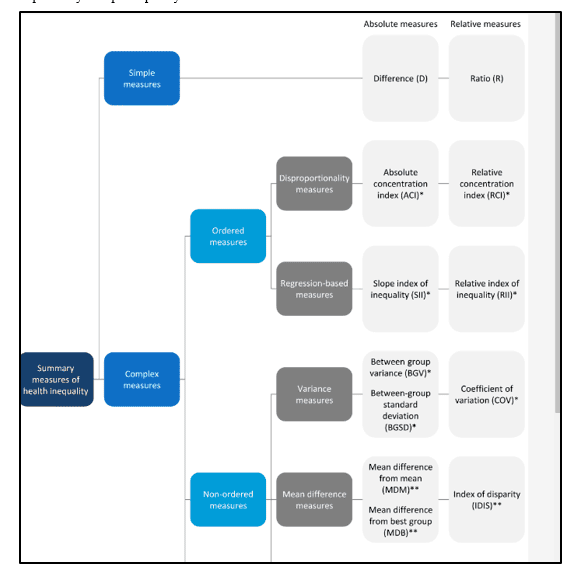
Figure 2: Healthcare inequalities
(Source: Schlotheuber and Hosseinpoor, 2022)
As stated by Schlotheuber and Hosseinpoor (2022), inequality refers to socioeconomic, geographic traits and demographics. Moreover, it can be also identified that structural theory helps to state inequalities in the outcome of health that are always caused by social differences. Moreover, health promotion also has a significant impact on a person's life and form where behavioral and cultural theory comes into practice. Hence this above picture has stated that indicating magnitude of inequality happens between subgroups of the population and retains units of health indicator. On that account, the above diagram has played a vital role in explaining poverty, mean differences, and regression-based measures.
The public health approach is a strategy that is based on the aim of developing the quality of health and life of the population. As opined by Khorram-Manesh et al. (2021), public health strategies help in adequate knowledge about diverse incidences and etiology in available management and also help in finding threats. Developing better PHS can help to translate diverse approaches for new skills and knowledge. Besides that PHS helps in evidence-based and cost-effective interventions that help in reaching everybody in a diverse population. Besides that, PHS also helps in working together and that helps in measuring problems and risk factors. Also, it helps in understanding diverse methods to prevent major risks. Along with those major goals PHS is also promoting education on health that helps in reducing or eliminating inequalities in the health sector.
For instance, developing health knowledge and reducing disparities in health inequalities helps in understanding the root cause of imbalances in socio-economics. Besides that PHS also plays a vital role in eradicating inequalities in public health hence better PHS needs to be implemented for setting balance in community health. As opined by McCartney et al. (2019), health is when a person's community and family can afford their income and power and education control a person's life. On that account in India, lack of nutrition, education, poverty, illiteracy, and low budget in the healthcare sector are some of the major factors of inequalities in the healthcare field. On that account eradicating poverty and developing the overall structure of the Indian healthcare system is highly important to mitigate inequalities in the health system of India. On that account, this essay will provide diverse policies and strategies that can help to develop the effectiveness of the healthcare system and also some tactics that can help mitigate major issues of poverty in healthcare.
In India, health inequalities are high as many people in India living under the poverty line have impacted their treatment process in the country. As per the view of Hindustantimes.com (2023), in India, over 415 million people will be moved to the poverty line within 15 years by 2005-2022. Besides that many children and adults are linked to malnutrition. As lack of malnutrition has impacted the lives of many people in India and made children weaker. An undernourished child can develop a weaker immune system that can increase susceptibility to illness and infection. Moreover, India has become the largest contributor of undernourished people across the world. As depicted by Feedingindia.org (2022), India has over 194.4 million which accounts for 14.37% of the overall population not having enough nutrition. As opined by Feedingindia.org (2022), in India over 36% of under 5-year children are stunted, 19% are wasted and over 32% of children are underweight in India.
Hence poverty is one of the major issues in India that has impacted the lives of people as many people can not eat a healthy diet. As opined by Thewire.in (2022) over 74% of Indians are not able to afford healthy meals in the country. On that account, poverty has limited the medical treatment process of poor people in the country which has directly impacted the overall number of poor people facing problems of diabetes in India. Low income and poverty have a direct relation with diabetes as diabetics are mostly seen in low and middle-income countries. As per the view of Gowda (2023), 75% of diabetic patients belong to low and middle-income countries. Hence rich people of India can use premium hospitals and doctors that helped them to recover from diabetic illness.
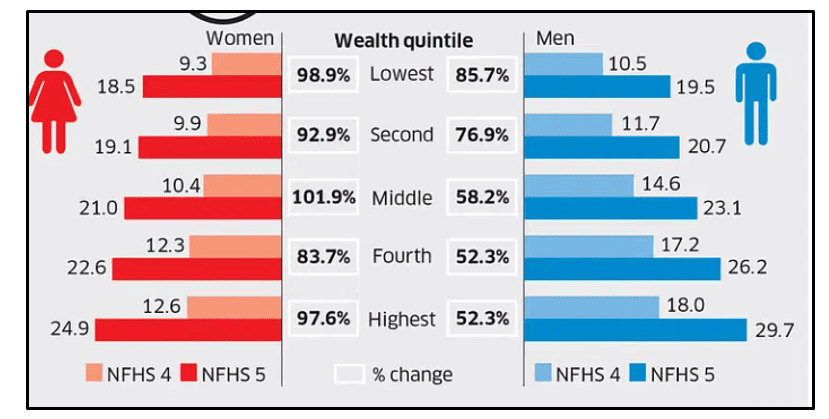
Figure 3: Rate of diabetes in rich and poor people of India
(Source: Gowda, 2023)
As per the report of NFHS Indian Medical Organisation surveys of 4 and 5 show that men and women who belong to poor families have seen a 37.5 % and 10% increase in the incidence of diabetes. On that account, the above diagram has shown the rate of diabetes in poor and rich people as the poorest people of the country have faced more concern regarding diabetes compared to rich people. Along with that lack of education, awareness is also a major factor that has increased healthcare inequalities in India. As many rural area people do not have basic knowledge of diabetes that becomes one of the major reasons behind their medical condition. As shown by Brahmapurkar et al. (2018), out of over 480 rural districts in India only 132 which accounts for over 27.5% of rural districts have a medical college. Along with that, Jharkhand, J&K, and Arunachal Pradesh do not have any medical colleges in their rural districts (BrahmapurKar et al., 2018).
Hence many districts of rural areas in India do not have a medical college that can help to mitigate the problems of locals. Moreover in India, rural parts of India that are poorer compared to urban and larger compared to urban have less number of doctors which shows health inequalities in the country. As stated by Pib.gov.in (2019), in India ratio of doctors and population is 1:1456 however there are huge differences in their distribution as urban to rural doctors ratio density is 3:8:1. Hence major number of expert doctors working in urban indian that played a vital role in enhancing numbers of diabetics patients in the country. On that account, the lack of doctors and education in rural areas has impacted the number of new patients of diabetics in India. As depicted by Dubey (2022), rural areas of India account for over two-thirds of India's population, still 33% of overall health workers, and only 27% of certified doctors are available in rural areas. This stat shows inequalities in rural and urban areas of India have created major problems. On that low income and poor people India faces health inequalities that have impacted their life expectancy and an increase in their mortality rate.
Addressing health inequalities in India requires comprehensive public health strategies, economic reforms, and increased medical accessibility. With Reliable Assignment Help for Students UK, learners can gain in-depth insights into healthcare challenges, ensuring well-researched and well-structured academic work on this crucial subject.
As per the view of Hill-Briggs et al. (2020), low income is directly associated with a higher risk of experiencing diabetic ketoacidosis in youth and adults with T1DM and also in higher Hba1c. On that account, eliminating poverty is a major aspect of controlling diabetes in poor patients. Thus the Indian government needs to provide diverse working opportunities and also needs to increase minimum wages in the country. As the rate of employment is high across parts of India it has played a vital role in developing diverse diabetic cases in the country.
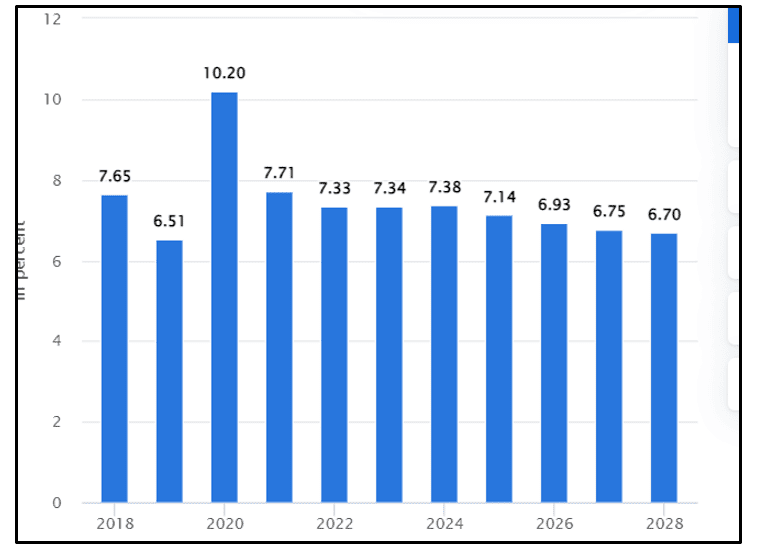
Figure 4: The unemployment rate in India
(Source: Statista.com, 2023a)
As depicted by Statista.com (2023a), in 2023 the rate of unemployment has reached over 7.34% in India. As stated by Statista.com (2023a), India is expecting to reach a country of 87.41 million people in 2023. Hence this above picture mentioned unemployment is one of the major problems of India that has impacted the lives of many people in the country. Moreover, the Indian government has tried diverse initiatives for developing rural India with the implementation of the "Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee policy”. It was one of the major anti-poverty schemes that helped to provide over 100 days of unskilled labor project work (Palamu.nic.in, 2019). However, this initiative did not make any major changes in the condition of rural people. Thus India needs to adopt new strategies to reduce the number of unemployment in the country. Therefore India needs to provide various education and skills training processes to under-revolutionary people of the country that can help to reduce overall poverty in the country. As in India, the skill gap is one of the major concerns as many students do not have technical training. In India over 93% of the population of India have not received any technical and vocational training as per the report of ( PLFS). India also needs to support small and medium-sized enterprises that can help to reduce the number of unemployed persons in the country. In India number of SMEs is low compared to other developing countries, which is the major reason behind the high unemployment rate in the country has increased poverty.
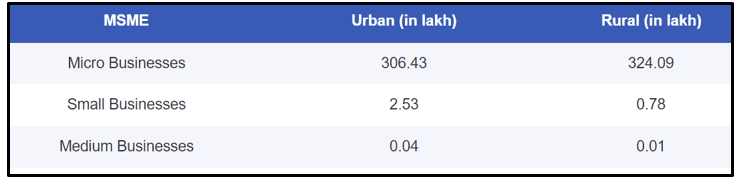
Figure 5: Numbers of SMEs in India
(Source: Tambe, 2023)
In India there are a total 3.3 lakh of SMe businesses that qualify as small businesses and in rural areas, there are 324.9 lakh businesses and in urban areas have 309 lakh businesses (Tambe, 2023). Hence India needs to promote more SME business in the country to provide various opportunities for poor people in the country.
Along with eliminating poverty India also needs to improve their overall healthcare sector as in rural areas there are limited numbers of good hospitals and doctors that have reduced access to healthcare in underdeveloped areas. Moreover, the Indian government has launched various policies and schemes to provide equitable access at affordable prices such as The NRHM ( National Health Rural Mission). It has helped to provide good quality medical services to underdeveloped social groups and regions. Moreover, the scheme has played a vital role in improving MMR and IMR and also provides diverse public services for nutrition and sanitation (Pandey and Mohan, 2019). However that scheme is also confined to north and eastern areas and J&K. Therefore in order to improve the condition of the health care system India needs to increase the number of doctors, hospitals, and nurses for the cure process of diabetics in the country.
As it has failed to increase the number of hospital doctors and nurses in the country. As analyzed by Ruralindiaonline.org (2022b), in 2021 India had only 764 district hospitals in the country. As stated by Ruralindiaonline.org (2022b), the average population of rural areas is 5734 people covered by one SC. Moreover, the Indian healthcare sector also needs to increase the number of specialist doctors in underdeveloped areas. In small hospitals, there were only 4,485 specialists against the requirements of 21,920 as per data from the government (Indiatimes.com, 2023). On that account, the Indian government needs to spend more on the development of the healthcare sector. As India currently spends around 1,25% of their overall GDP on healthcare (Ruralindiaonline.org, 2022a). Hence the Indian government needs to spend around 3% of its overall GDP to mitigate such poor infrastructure of Indian healthcare.
Conclusion
Eliminating Health inequalities is a responsibility for every sector hence reducing Health inequalities is the most important objective. As it provides a diverse opportunity to adapt diverse health-related policies that can help to develop a positive impact on any healthcare sector. In India Health inequalities are major problems that impact the lives of many people in the country because of lack of money. Hence poverty in India is connected to Health inequalities in India as well and poverty has limited a large section of the country to having a better healthcare process. Thus the Indian government needs to explore diverse policies that can help to reduce Health inequalities in the country. However Indian government has tried many strategies to mitigate Health inequalities that have worked for many people in the country. However, there are still too many loopholes that are increasing Health inequalities for Indian people.
Recommendation
References
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking Assignment Helper services. The...View and Download
Introduction Get Free Online Assignment Samples from UK's Best Assignment Help Experts to boost your academic...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction - The Role of Budgeting and Finance in Organizational Management Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking Assignment Help...View and Download
Copyright 2025 @ Rapid Assignment Help Services
offer valid for limited time only*

