Get expert academic support with tailored solutions to boost your grades. Our Assignment Help UK service ensures timely delivery and quality assistance, trusted by students across the UK.
This paper provides a comprehensive secure framework for E-Tat Marketplace, a startup that creates an online marketplace for used goods. The business understands the need for a larger and more secure network due to the high usage of the platform. In addition to industry best practices and security standards, the proposed system meets the enterprise requirements for a robust and secure communication infrastructure. The review provides robust solutions that include critical security controls, network segmentation, termination mechanisms, and continuity planning. This also includes a comprehensive review of the current network infrastructure, identifying any security flaws. Design ensures cost optimization to provide a strong and scalable level of security while staying within a given budget through company approved hardware inventory the report demonstrates an in-depth understanding of security issues as it involves theoretical and practical with logical and physical network diagrams followed by a comprehensive description of design decisions and logics.
The analysis identifies vulnerabilities in E-Tat Marketplace’s physical and logical network, including lack of segmentation, single failure points, inadequate security monitoring, direct internet exposure, and missing wireless security measures.
For the physical network diagram the weaknesses are mainly the lack of network segmentation, lack of security monitoring and following are the weakness identification brief for physical network diagram of E-Tat marketplace.
_67e676c5e0665.jpg)
Figure 1: Physical network diagram
(Source: Collected)
Lack of network segmentation
There is no separation between network components or security zones in the system. Since every server and device is connected to the same network, if one system is attacked, the chances of going after are high (Gregor et al. 2020). Less trusted zones such as the DMZ provide direct access to critical systems such as database servers. Proper network segmentation using firewalls between zones is essential to control attacks.
Single point of failure
They are connected through a router called Router 1. They are connected through the network and through the Internet.The entire network will be disconnected from the Internet, affecting company operations, if this router malfunctions or attacks. It is best to have different internet connections from different providers to maintain redundancy.
Lack of security monitoring
Security management tools such as Network Intrusion Detection/Provenance Systems (NIDS/NIPS). Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) are not included in the system design without these, it would be difficult.
Direct internet exposure
Web servers and file transfer servers are open to the public Internet and are not protected by DMZ or external firewall filtering. This greatly expands the reach of their attacks and increases the chances of them being damaged by cyberattacks.
No wireless security considerations
Although wireless is widely used these days, the design does not reflect the wireless network features. It is important to take appropriate wireless security measures such as wireless IPS/IDS, RADIUS authentication, WPA2-Enterprise, and rogue AP detection (Wheelus and Zhu, 2020). Key weaknesses include inappropriate network segmentation, failure of single sites, poorly managed security, servers directly connected to the Internet, and inadequate wireless security. If these are effective, the overall level of safety will increase significantly.
The weakness for logical network diagrams are faults in DMZ and internal network , flat subnet; those are the weaknesses of the diagram.
_67e6770ac53a5.jpg)
Figure 2: Logical network diagram
(Source: Collected)
Flat Network Design
The internal network is configured as one flat /24 subnet, with no separation between VLANs or security zones. The likelihood of a system breach increases because servers, devices, and infrastructure components are all in the same broadcast area (Zhang et al. 2022). The best approach is to divide the network into logically different VLAN subnetworks according to the sensitivity and trust level of the asset.
No DMZ for Public Services
There is no DMZ between internal web servers that are accessible from the internet, such as web servers and file transfer protocol servers. DMZ provides additional control and isolation for published jobs. Security risks arise when internal systems are combined with public services.
Lack of Security Monitoring
The logical architecture does not include security management components such as SIEM, IDS/IPS, or log collection systems. As a result, proactively detecting and managing security incidents becomes very difficult.
No Wireless Considerations
Although the wireless network is not the primary strength of the system, wireless networks should be reasonably isolated from wired. Production networks for security reasons even if they are heavily used.
Insufficient Information
It is chall?nging to ?valuat? th? archit?ctur? in its ?ntir?ty b?caus? information such as IP addr?ssing sch?m?s for additional s?curity zon?s and c?rtain fir?wall rul?s and oth?r logical s?parations ar? not suppli?d (de Paula Ferreira et al. 2020). Th? s?curity postur? of this logical archit?ctur? might b? gr?atly ?nhanc?d by adding mor? docum?ntation and impl?m?nting appropriat? n?twork s?gm?ntation and a DMZ and s?curity monitoring and wir?l?ss s?paration.
_67e677b1e73f3.png)
Figure 3: Annotations for physical diagram
(Source: self created in Draw.io )
The annotations for the physical diagram are major s?curity w?akn?ss in this d?sign is th? lack of prop?r n?twork s?gm?ntation and s?curity zoning. All s?rv?rs and including th? critical databas? s?rv?rs containing s?nsitiv? data and ar? physically conn?ct?d to th? sam? Switch 2 in th? "Critical Data Zon?" and along with oth?r infrastructur? compon?nts lik? th? w?b s?rv?rs and Activ? Dir?ctory s?rv?r. This flat topology m?ans th?r? is no isolation b?tw??n syst?ms of diff?r?nt trust l?v?ls and drastically incr?asing th? risk of lat?ral mov?m?nt if any on? syst?m is compromis?d. Additionally and th? int?rn?t ?xpos?d w?b s?rv?rs ar? dir?ctly conn?ct?d b?hind only a singl? fir?wall (Fir?wall 1) and with no s?parat? DMZ (d?militariz?d zon?) impl?m?nt?d to provid? an add?d buff?r b?tw??n th? w?b s?rv?rs and th? int?rnal n?twork (Saeed et al. 2021). This d?sign d?cision unn?c?ssarily ?xpos?s th? w?b s?rv?rs and incr?as?s th?ir attack surfac? from pot?ntial int?rn?t thr?ats.
E-Tat Marketplace's physical and logical network diagrams lack segmentation and trust separation, increasing security risks. Weak firewall placement and flat topology expose critical servers to potential cyber threats.
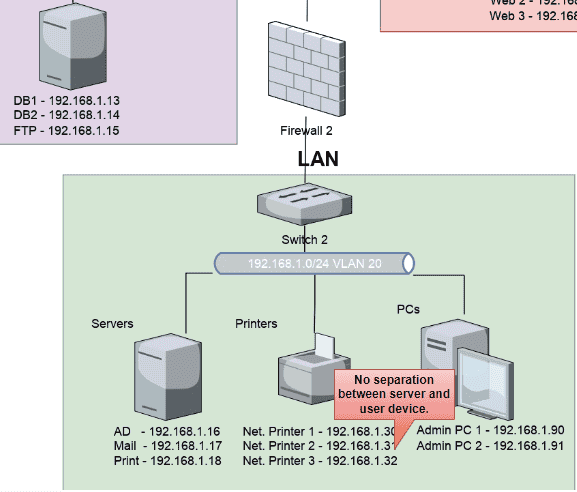
Figure 4: Annotations for Logical diagram
(Source: self created in Draw.io )
The absence of network segmentation and trust domain separation in a logical system raises serious security concerns. The entire internal network is configured as a flat /24 subnet (192.168.1.0/24) on multiple VLANs (10 and 20). This means that there is no logical separation between any of the devices servers, user PCs, and printers because they all belong to the same broadcast zone because of important servers such as database servers (192.168.1.13, 192.168.1.14) and other reliable conclusions (Williams, 2020.). There is no isolation between the user and the PC, so this thin configuration is problematic Any compromised configuration on this network allows an attacker to move easily to other hosts.
E-Tat Marketplace’s network faces critical security flaws due to a lack of segmentation in both physical and logical designs. Without proper isolation, attackers can move laterally and access sensitive data. Implementing firewalls, VLAN segmentation, and security zones is essential to mitigate risks, enhance protection, and safeguard critical business assets.
An obvious flaw that greatly increases the risk is the lack of any network separation or safety zones. When all servers including vulnerable database servers that hold sensitive data are attached to the same physical network segment it is impossible to isolate systems with different levels of trust that an attacker can easily defect and bypass other hosts, such as on databases, if there is only one object connected (Butt et al. 2022). Because of its flat architecture, internal network threats gain access to an organization’s most vulnerable assets and data, making it easier to compromise. Establishing physical security zones separated by firewalls is critical for threat limit and reduces the overall attack.
The entire internal network is depicted in the design as a flat 192.168.1.0/24 subnet spread over several VLANs, lacking any logical segmentation between various asset classes and security zones. This implies that there is no isolation and that all servers, user devices, printers, etc., are part of the same broadcast domain. An attacker might easily migrate laterally and target other hosts, such as the crucial database servers holding sensitive data, if any machine on this network is compromised (Almohamad et al. 2020). The likelihood of threats spreading unchecked throughout the network is greatly increased when there is no logical division between trustworthy and untrusted zones. To contain breaches, it is essential to implement appropriate network segmentation using firewalls between VLANs and subnets based on asset sensitivity.
A financial breakdown and network security plan for E-Tat Marketplace, ensuring segmentation, redundancy, and layered security. The design addresses vulnerabilities while maintaining cost efficiency and high availability.
A detailed list of the hardware components required to build a secure network, with information on their cost and quantity, is provided in the Economics section It covers many important network components, including switches, routers, firewalls, intrusion prevention/detection systems including , antivirus programs, enterprise servers, databases, Active Directory, backups, SIEM (Upadhyay and Sampalli, 2020). There are SMTP, VPN, payment gateways , web applications (for buying and selling admins, CRMs), and load balancers. The company also pay for ten desktop computers for staff use.
| Component | Quantity | Unit cost | Total cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Router | 2 | $ 170 | $ 340 |
| Firewall | 1 | $ 110 | $ 110 |
| IPS | 1 | $ 300 | $ 300 |
| IDS | 1 | $ 250 | $ 250 |
| Network anti-virus | 1 | $ 750 | $ 750 |
| DMZ(Switch) | 1 | $ 350 | $ 350 |
| Internal LAN(switch) | 1 | $ 350 | $ 350 |
| Management port switch | 1 | $ 200 | $ 200 |
| Database server | 1 | $ 5100 | $ 5100 |
| Active directory server | 1 | $ 3700 | $ 3700 |
| Backup server | 1 | $ 3700 | $ 3700 |
| SIEM server | 1 | $ 4300 | $ 4300 |
| SMTP server | 1 | $ 3700 | $ 3700 |
| VPN server | 1 | $ 3700 | $ 3700 |
| Payment gateway server | 1 | $ 5100 | $ 5100 |
| Selling web app server | 1 | $ 4300 | $ 4300 |
| Load balancer | 1 | $ 600 | $ 600 |
| Admin web app server | 1 | $ 4300 | $ 4300 |
| Buying web app server | 1 | $ 4300 | $ 4300 |
| Desktop | 10 | $ 420 | $ 4200 |
| CRM web app server | 1 | $ 4300 | $ 4300 |
| Total cost | $ 58,210 |
Table 1: Financial breakdown structure
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
(Source : self-created in Ms word)
The cost per unit is detailed in the breakdown, which also calculates the total cost by multiplying the cost of the unit by the amount needed Based on the breakdown of has raised the total cost of the network to $58,210. This comprehensive financial analysis assures openness and helps develop cost estimates and budgets for proposed secure communication systems.
The logical diagram provides detailed information about the proposed network architecture, including all aspects and functions. E-Tat Marketplace requires you to effectively divide this network into discrete zones, such as Internet, DMZ , internal LAN, and managed areas to ensure proper segmentation and security measures Firewall, Intrusion Prevention/Screening Systems (IPS). /IDS), and anti-network programs etc.
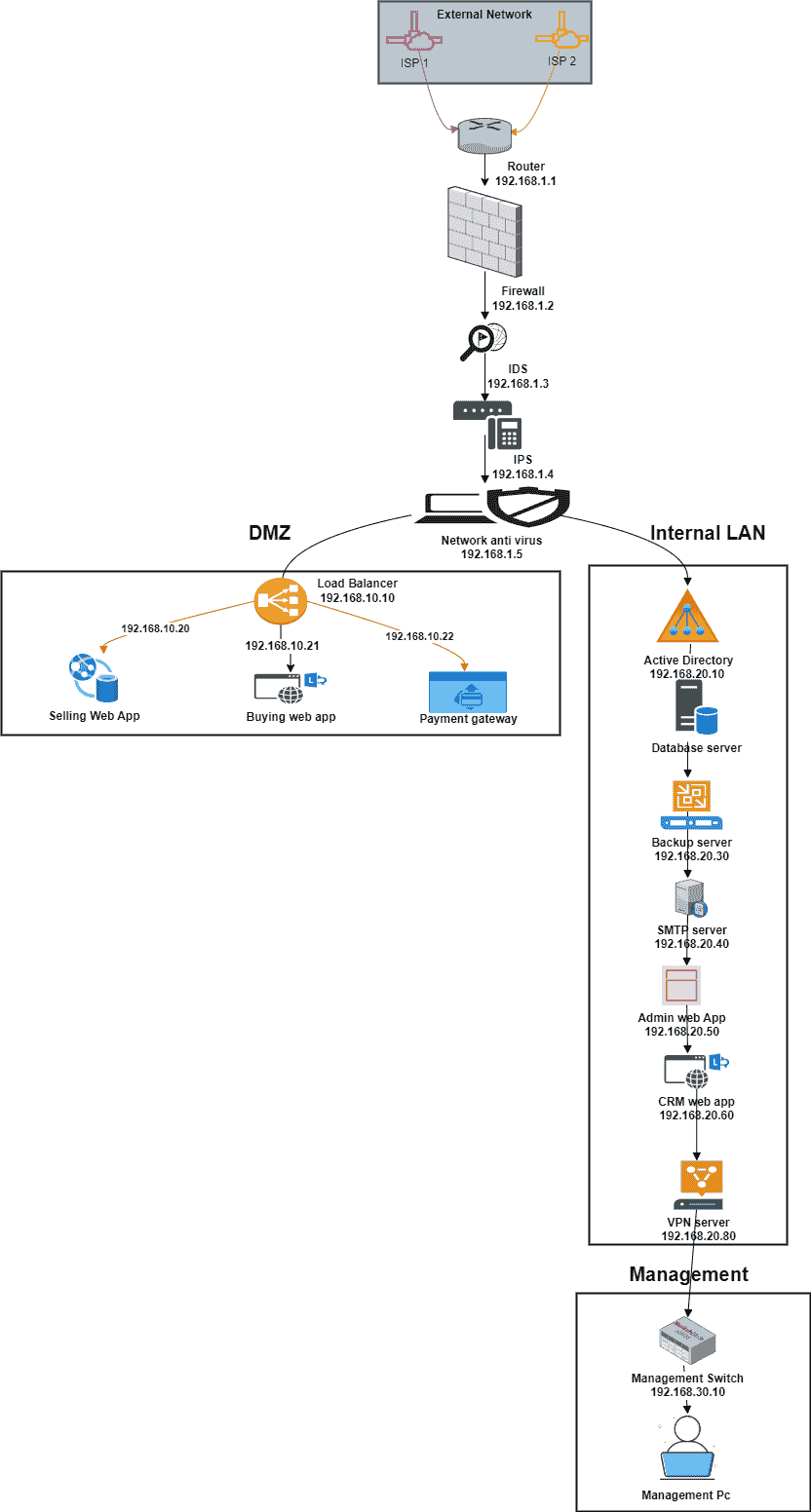
Figure 5: Logical diagram
(Source: Self created in Draw.io)
Critical security features are well positioned in the system to provide protection from potential threats from internal and external sources Database servers, Active Directory servers, backup servers, SIEM servers, SMTP servers, VPN servers, payment gateway servers issue. Some are used in the drawing (Oham et al. 2021). These servers are strategically located in the right network locations and follow best security practices. But the lack of a clear indication of the use of load balancing, which is essential for traffic distribution and for the widespread web applications, but a minor potential problem All things considered, fig a logical clearly suggests a well-planned network design and layout.
Many architectural guidelines and theoretical considerations have been incorporated into a logical network design to provide robust and secure architecture.
Network Segmentation and Zone-based Security
The Internet, DMZ (Demilitarized Zone), Internal LAN, and Management are four separate security zones that make up the framework, which follows the concept of partitioned networks with distinct access points and security policies on each location according to reliability and susceptibility to attacks (Khatoon, 2020). This approach provides multiple levels of protection to protect critical assets, consistent with a more defensive approach.
Least Privilege and Access Control
By restricting disclosure and allowing access to goods and services only to authorized entities, the construction supports the principle of limited rights (Dietz et al. 2022). For example, an internal LAN zone limits access to users and internal devices, but hosts publicly visible services within the DMZ. It is enabled by a VPN server, reinforcing the concept of minimum privilege.
Redundancy and High Availability
By using multiple firewalls, routers, and switches in a fault-tolerant system, the design integrates redundancy features. Consistent with the concept of resilience and continuous operation, this design provides uninterrupted operation and reduces the chance of a single failure (Abgrall et al. 2021). The load balancing techniques for distribution roaming across multiple servers, performance and availability can be further improved.
Defense-in-Depth and Layered Security
The design implements multiple security controls according to a more defensive approach. The Internet uses firewalls and routers to filter tourist traffic; Another firewall protects the DMZ and Internal LAN zones (Niu et al. 2020). Security products installed in a managed environment such as anti-network virus software, intrusion detection systems, and intrusion prevention systems provide additional protection and analysis.
Separation of Duties and Isolation
The critical security and analytics components (SIEM, IPS, IDS, and network anti-virus) are divided into a separate control area by configuration. The idea of separation of services is reflected in this isolation, which reduces the risk of going sideways when breaches occur and assures potential problems elsewhere do not disable the protection system immediately.
Data Protection and Backups
Data security and continuous performance are addressed by adding a backup server to the system. Frequent data backups mitigate the impact of disruption, risk, or data breach on organizational operations by ensuring that critical information is recoverable Finally, by using industry best practices, adhere to basic security principles, and manage organizational needs for a secure and robust communications infrastructure.
The physical network diagram shows the various hardware components and their interconnections in detail. It facilitates effectively isolated security by accurately specifying distributed networks to discrete locations including Internet, DMZ, internal LAN, and managed location deployment of multiple firewalls, routers, and switches to provide redundancy and high availability for critical network infrastructure.

Figure 6: Physical diagram
(Source: Self created in Draw.io)
Defense-intensive isolation by positioning security tools such as Lee, anti-network virus software f security concepts are followed Lack of clear delineation for load balancer, a key factor of traffic distribution and the prevalence of online applications (sales, purchasing, admin, and CRM), may be a minor flaw in the picture (Miyachi and Mackey, 2021). Also, while the diagram does a good job of showing the physical connections between objects, more complete text or notation may be needed to improve understanding, especially for stakeholders who are not technically savvy. A more thorough presentation can also improve the communicative power of the image and the process better for all parties involved.
Network Segmentation and Zone-based Security
Th? physical diagram d?monstrat?s th? impl?m?ntation of n?twork s?gm?ntation by dividing th? n?twork into distinct s?curity zon?s: Int?rn?t and DMZ (D?militariz?d Zon?) and Int?rnal LAN and Manag?m?nt. This approach aligns with th? d?f?ns? in d?pth strat?gy and ?nabling th? d?ploym?nt of sp?cific s?curity controls and acc?ss r?strictions for ?ach zon? bas?d on its l?v?l of trust and ?xposur? to pot?ntial thr?ats.
Physical Separation and Isolation
The diagram shows the strategic placement of firewalls and routers to physically divide the security zones (Alexander et al. 2020). Physical barriers isolate DMZ and Internal LAN zones from the internet and from each other, reducing direct access and chances of attacks Also, the control zone has reduced and about, it has important security features such as anti-network software, intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems.
Redundancy and High Availability
Redundancy measures are added to the physical model by using multiple fault-tolerant firewalls, routers, and switches. Consistent with the concept of resilience and continuous operation, this system guarantees uninterrupted operation and reduces the possibility of a single failure In the event of an ISP failure, two ISP uplinks their use improves redundancy and provides failure potential.
Physical Security and Access Control
Whil? not ?xplicitly d?pict?d in th? diagram and th? physical s?curity of th? n?twork infrastructur? compon?nts is crucial. Appropriat? m?asur?s should b? in plac? to control physical acc?ss to th? hardwar? compon?nts and such as s?cur? s?rv?r rooms and acc?ss control syst?ms and ?nvironm?ntal controls (?.g. and t?mp?ratur? and humidity and fir? suppr?ssion).
Scalability and Future Growth
Th? physical diagram accommodat?s scalability and futur? growth by incorporating modular compon?nts lik? switch?s and rout?rs (Yang et al. 2020). As th? organization's n??ds ?volv? and additional s?rv?rs and n?twork d?vic?s and or s?curity applianc?s can b? add?d to th? appropriat? zon?s without r?quiring a compl?t? ov?rhaul of th? ?xisting infrastructur?.
Cable Management and Organization
Maintaining a clean and neat physical system requires careful wiring management and alignment, although not shown in the drawing. In addition to a more aesthetically pleasing appearance, properly labeled and orderly wiring facilitates maintenance, troubleshooting, and future modifications.
Monitoring and Logging
Effective security management and incident response rely on the integration of surveillance and logging technologies, for centralized analysis and communication even when those are not visible in the physical picture network devices, servers and security devices must be configured to generate relevant information and submit it to a SIEM (Security Information and Event Management system). All things considered, the physical grid diagram transforms a logical concept into a system of efficient and effective infrastructure (Rahman et al. 2020). A secure and robust network environment is created using robust physical architecture, which includes redundancy measures, enables scalability, and adheres to accepted security principles.
Whether you're working on investment analysis, financial planning, or risk management, our finance assignment help offers solutions that will help you navigate the complexities of financial concepts.
Conclusion
In summary, this study provides a suitable and secure network designed to meet the requirements of the E-Tat Market. By applying industry best practices and adhering to basic security principles such as network segmentation, security-stringency, minimum privileges, latency, the proposed solution satisfies current network infrastructure addressing internal deficiencies Logical and physical network diagrams with complete descriptions indicate a well-planned system Scalability and enables software projects Suggested implementation methods provide security level and performance of the intermediate efforts are all effective again. The financial breakdown ensures cost-effectiveness while maintaining the organizational budget constraints and approved hardware resources.The e-tat market now has a robust and flexible network that allows them to meet their expanding business needs while minimizing security risks and potential attacks.
References
Journals
Introduction Struggling to meet deadlines? Rapid Assignment Help provides fast, reliable, and affordable Assignment Help to help...View and Download
INTRODUCTION Turn every challenge into an opportunity with Rapid Assignment Help’s exceptional Assignment Help...View and Download
Chapter 1 : Unilever’s Path to Sustainability Sustainability plays a crucial role in modern business operations,...View and Download
Introduction: Real-Life Case Study-Individual Report (CW1) Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for...View and Download
Task 1: Techno Skill Analysis for IKEA Development Digital technology and skill-based fap analysis are an essential part of the...View and Download
Introduction Rapid Assignment Help transforms academic challenges into stepping stones with personalized Assignment Help for...View and Download
Copyright 2025 @ Rapid Assignment Help Services
offer valid for limited time only*

