Get Professional Assignment Help for All Subjects to enhance your understanding of IKEA’s technological advancements and business strategies with expert guidance.
IKEA, the global furniture and home furnishings company, is comprehensively seen for its innovative business model considering sensible, modular flat-pack furniture that customers assemble themselves. This model has fueled IKEA's fast global expansion and strong growth over numerous years. In any case, IKEA faces increasing challenges in the current dynamic, significantly competitive environment driven by digital disruption, demanding consumers, and sustainability pressures. To sustain its success, IKEA needs to innovate across all aspects of its business continuously. This task embraces such a gap assessment for IKEA. It utilizes exhibited analytical approaches like SWOT analysis, benchmarking, and scenario planning to ponder IKEA's current technology and skills rather than emerging needs. The analysis uncovers key priorities and recommendations to guide IKEA's innovation attempts.
A couple of procedures exist to conduct a systematic technology and skills assessment. Each approach gives an undeniable perspective that together facilitates a comprehensive analysis.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT framework evaluates internal strengths and weaknesses close by external opportunities and threats. SWOT analysis can stock existing legitimate assets like focus technologies, capable agents, restrictive techniques, and digital frameworks. These location strengths that IKEA can utilize. Of course, weaknesses could consolidate out-of-date legacy frameworks, lack fitness in key locales, nonattendance of data pieces of information, inefficient cycles, or other capacity gaps (Alves, and Luís Reis, 2020). Furthermore, inspecting the competitive scene and greater environment to pinpoint emerging opportunities as well as true to form disruptions. Significant opportunities for IKEA consolidate rising eco-conscious consumers, emerging markets, innovative production technologies, and digital/Omni channel retail. Threats encompass competitors, moving demographics, disruptive business models, economic volatility, and regulatory changes.
Benchmarking
Benchmarking systematically checks company execution and capacities against enemies and top-level models both inside and outside the business. These external perspective elements limit gaps versus pioneers. Huge benchmarking approaches consolidate cycle benchmarking to evaluate utilitarian adequacy, effectiveness, consistency, and various estimations related to focus business processes like gathering, course, publicizing, and thing progression (Haraldsson, et al. 2020). Key benchmarking to assess and ponder definitive capacities like innovation, agility, branding, customer experience, and sustainability.
Foresight Techniques
Foresight techniques offer approaches to systematically explore future examples, disruptions, and scenarios. They move analysis from receptive to proactive. Foresight techniques consolidate environmental checking to recognize early signals of emerging political, economic, social, technological or regulatory changes on the horizon. This expects threats and opportunities right now to reply. Scenario planning to make strong hypothetical future universes considering weaknesses and examples. Particular records of potential destinies uncover new challenges and possible results. Technology expecting to anticipate how existing and emerging technologies could progress (Aguilar, 2022). This elements coming limits close by potential consequences for things and business models.
Don’t let challenging business concepts hold you back—our business assignment help equips you with the necessary knowledge and tools to tackle your assignments and excel in your course.
SWOT Analysis
| Strengths | Opportunities |
| Key strengths in its unique value-based business model Recognizable brand identity Non-expensive affordable product design Sophisticated logistics network |
Huge opportunities to expand in developing markets Enhance customer experience through digitalization Lead environmentally sustainable practices Leverage emerging technologies like automation, robotics, and 3D printing across operations |
| Weaknesses | Threats |
| Significant weaknesses include poor e-commerce maturity Limited customization choices Complex assembly requirements for customers Add sustainability practices |
Approaching threats come from lower-priced competitors Online-local rivals Demographic changes in key markets Reduced consumer loyalty |
Table 1: SWOT Analysis
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
Strategic gaps become apparent in digital capabilities and customer experience relative to market opportunities as well as the sustainability gap considering IKEA's brand values. Benchmarking and foresight analysis will further investigate these gaps.
Benchmarking
The benchmark analysis of IKEA mainly Include:
Processing the benchmarking against leading retailers features the company’s dispersion and inventory management strengths and also reveals gaps in areas like warehouse automation, data examination, and online fulfilment where leaders generally invested heavily.
Strategic benchmarking versus top consumer brands mainly uncovers gaps in customer experience and loyalty programs.
Competitive benchmarking always shows production cost advantages and also exposes gaps in e-commerce convenience, speed, and personalization relative to online rivals.
Functional benchmarking mainly certifies gaps in digital marketing, data science capabilities and sustainability initiatives compared to progressive practices.
Foresight Analysis
The foresight analysis of potential futures mainly focuses to several gaps. Also, scenario planning features the strategic risks expecting that IKEA fails to adapt meeting diverse consumer preferences across generations and cultures model. Technology forecasting also suggests gaps in capabilities to harness emerging technologies to change production, dissemination, and business model innovation (KUMAR, 2023). AI, automation, robotics, drones, and AR/VR, these all are the example of unrealized potential. Product road mapping mainly reveals gaps in smart furniture, sensors, and data analytics as well to provide personalized customer experiences and anticipate needs. This foresight stresses the gaps posed by IKEA's legacy business model in the face of accelerating change.
This gap assessment mainly illuminates five key innovation areas where IKEA ought to boost capabilities and skills:
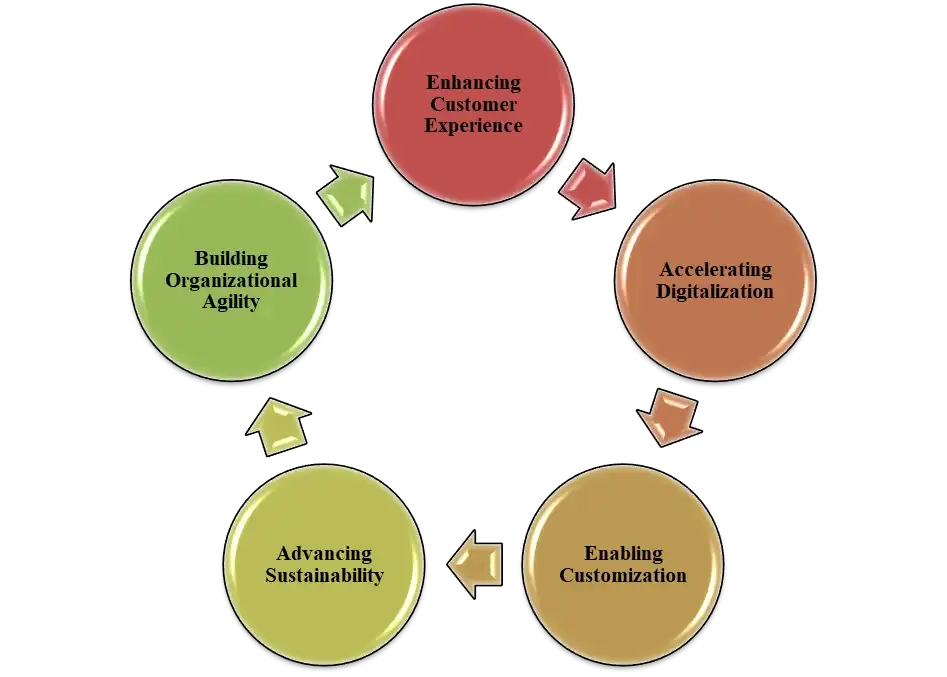
Figure 1: Development Areas
Enhancing Customer Experience: IKEA mainly suffers from a gap between consumer expectations and genuine encounter caused by obscure directions, precarious assembly, and absence of service. Addressing this requires innovations for the enhancement of product use for customers. Possibilities mainly include Intuitive modular furniture components engineered for self-assembly (Gustafsson, and Olmarker, 2021). Quick connect features can minimize assembly time also. Immersive 3D interactive guidelines and AR-assisted assembly mainly make the process easier and error-free. Investments in robotics to enable automated or self-assembling furniture mainly eliminate customer disappointment during the business operations. Delivering on customer experience remains an innovation need for IKEA for facing the challenge of adjusting cost and convenience in their operations.
Accelerating Digitalization: IKEA mainly focusing in leveraging digital channels, data and connectivity across its business which is influential for get up to speed mainly. Key directions also include expanding online stage capabilities for Omni channel operations, enriched customer journeys and digital personalization (Elizaveta, 2021). Deploying automation, robotics, analytics and AI across production can mainly store network and inventory management to boost efficiency in the business. It also need to build smart warehousing infrastructure with real-time inventory transparency and automated fulfillment. While digitalization impact in financial investment, it is table stakes for competing today and realizing new opportunities properly.
Enabling Customization: IKEA's standardized products fail to meet rising consumer demand for personalization and localization. Potential arrangements also include agile production systems and innovative digital creation like 3D printing to beneficially produce little batches and custom structures (Chichilanov, 2022). This device can be configurator for consumers to customize finished goods, also textures, and features of the goods. Data-driven personalization is for recommend tailored offerings which align with individual needs of customers. Also, the customization mainly permits premium estimating but also requires offsetting product variety with operational efficiency.
Advancing Sustainability: There are some limitations of IKEA to find and bridge key gaps in overseeing environmental effects across its operations and production network. Innovation opportunities can mainly include obtaining and using sustainable materials like recyclable thermoplastics, eco-friendly textures, and bio-based composites (Ding, et al. 2021). Also, eliminating hazardous chemicals from production processes through green chemistry and non-toxic materials. Leveraging IoT sensors, data analytics and block chain transparency to screen environmental footprints for the top to bottom review of the value chain process.
Building Organizational Agility: The legacy hierarchical structure of IKEA mainly restricts the agility of respond to diverse global markets and local customer needs of the firm. Boosting agility mainly involves empowerment of country relationship to address unique regional differences rather than one-size-fits-all central planning (Al-Zghool, 2020). While agility enables localization, it should balance benefits against the need for primary efficiency of the operations.
These all strategic domains mainly offer compelling innovation opportunities for IKEA to reinvent itself which can meet emerging challenges and rekindle growth .
This gap analysis also found some strategic recommendations for IKEA's innovation center:
The main objective of the firm is to enhance end-to-end customer experience. Also, deploy technologies like AR, digital instruments, and automation to rearrange and personalize product selection, representation, and assembly.
Also, promoting digital transformation initiatives process to boost operational efficiencies. It also expand online channels and harness data-driven experiences. It mainly exists in areas like fulfilment automation, augmented reality show areas and digital customization.
Pursue modular product architectures for the improvement of enabling mass customization process.
The roadmap can also adjust short and long-term objectives which mainly recommended to pace critical investments (Beqiri, 2020). IKEA ought to commit now to developing the new skills and competencies essential for future competitiveness and growth.
Sustainable success mainly requires expecting change and also closing strategic capacity gaps. This demands innovation to elevate customer experiences, embrace digitalization, customize offerings which mainly protect the environment and change affiliation wide agility. Executing on these priorities by leveraging emerging technologies and building new skills will situate IKEA to prosper in the years ahead as a purpose-driven brand. This gap analysis provides a data-driven framework to guide IKEA's next chapter of evolution, growth and industry leadership.
An innovative solution worth assessing is the use of augmented reality (AR) capabilities to help and work on the shopping and assembly process for customers. This emerging technology also holds strong potential to close IKEA's main customer experience gap.
Applying AR all through the customer journey could permit IKEA to break new ground in the retail experience:
In-store shopping: AR visualization would let customers digitally preview furniture in situ. Overlay tones, setups and arrangements (Bernhard, 2021). Also accurately assess products for the customers to their homes as well.
Planning: AR applications could provide room measurement capabilities, interactive configurations and interior design visualization to improve on planning.
Navigation: In-store navigation features would guide customers to desired products and inventory availability using indoor mapping. It also reduce the disappointment of the firm.
Information: Contextual product data, user manuals and specifications could be summoned on demand through AR overlays and markers. Aid decisions.
Assembly: AR instructions can provide animated step-by-step visual guidance projected onto parts during assembly at home. Reduce errors. Permit two-handed assembly without flipping pages. Offer voice orders and feedback.
Community: AR-based networking could enable crowdsourced help to solve assembly issues. Connect customers to share tips and advice.
Customization: Co-creation AR configurators would permit personalized product design with previews. Visualize choices.
Capabilities required to enable AR include:
Hardware: AR-optimized devices like smartphones, tablets, and smart glasses. Handhelds suffice initially, however wearables will maximize benefits.
Software: AR engines, 3D visualization capabilities, physics simulation, and development platforms.
Connectivity: High-bandwidth networks like 5G and Wi-Fi to deliver immersive experience through distributed computing and content delivery (Parbat, et al. 2021).
Data: 3D models, product information, instruction rationale, and user data to power contextual experiences.
Sensors: Cameras, depth sensors, GPS and IMUs to map environments and locate users.
Interface: Intuitive UI/UX design for regular user interactions with virtual elements through touch, voice and gestures.
IKEA is well positioned to deploy AR across its business in phases given its emphasis on digitally-vigilant consumers, in-home experience, and DIY assembly.
The Implementation of AR-driven innovations in the firm can produce main valuable benefits for IKEA across key dimensions. Here are the Examples of those implementations as follows:
Personalization: Customers can choose products digitally with personalized design choices not feasible with large scale manufacturing. AR configurators mainly permit co-creation aligned to personal taste.
Convenience: AR shopping apparatuses also enable customers to accurately assess, ease selection, and work on their planning. In-store navigation and information also access ads convenience. Home assembly is much easier for the customers to fulfil their requirements.
Engagement: Interactive AR experiences mainly boost engagement across channels. IKEA are becoming a lifestyle destination beyond genuine stores. Their community connection process also deepens the brand loyalty of them.
Agility: Quick AR prototyping can also accelerates product innovation and testing. New designs enhance the market speed by leveraging simulations and digital creation in their manufacturing.
Sustainability: AR usage analytics and digital-first experiences which mainly reduce paper waste. Carbon footprint also shrinks by cutting unsuccessful purchases and product returns.
These potential benefits make AR-centric customer experience enhancements a compelling innovation require for IKEA (Strömstedt, and Vaagenes Rehmberg, 2021). The purposeful implementation mainly serves to close the digital technology gap which identified in this gap analysis of the firm. AR technique can also provide a growth stage to reconnect IKEA with contemporary consumers by revolutionizing their method for purchasing.
While implementing the AR innovations in the firm, it mainly faces some technological, design-related, and strategic challenges. Here are those challenges:
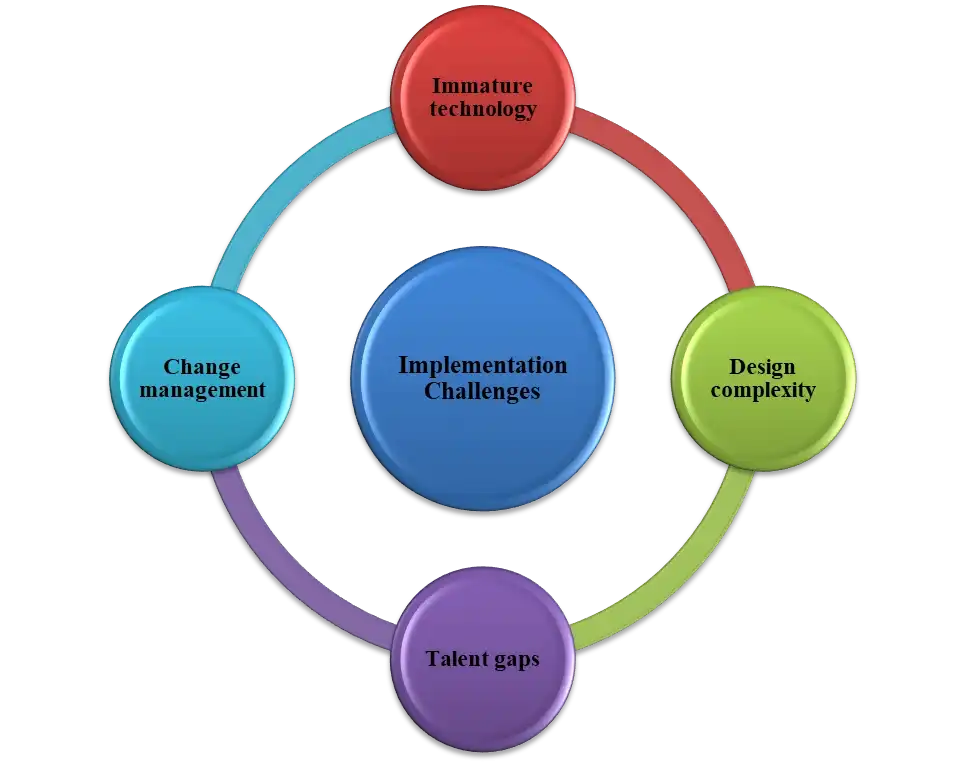
Figure 2: Implementation Challenges
Immature technology: Current AR hardware, software, connectivity and UX capabilities are mainly counted in limited resources. Performance issues also need resolution. The availability of Smart glasses also need scale.
Design complexity: Photorealistic 3D models, accurate physics simulations, precise tracking and environmental mapping mainly require basic content development efforts.
Talent gaps: IKEA will need specialized skills in areas like computer vision, 3D environment modeling, and UX design and data integration. Momentary gap might be require partnerships and upskilling for the better outcome.
Change management: Transitioning to AR-first processes inside the customer touchpoints will meet organizational resistance in their operations (Johansson, and Härdig, 2020). The training of users in these unfamiliar AR practices are most essential duty of the firm.
The barriers for implementing AR process in IKEA also need to be identified properly. Insightful change management and phased implementation can be the main key to addressing the challenges.
IKEA possesses a distinctive value-driven culture emphasizing moderateness, sustainability and Scandinavian straightforwardness. This process can mainly boost standardization and consistency (Paulshepherd, 2024). Adopting disruptive AR technologies can also face internal resistance for some reason. Here are those reasons:
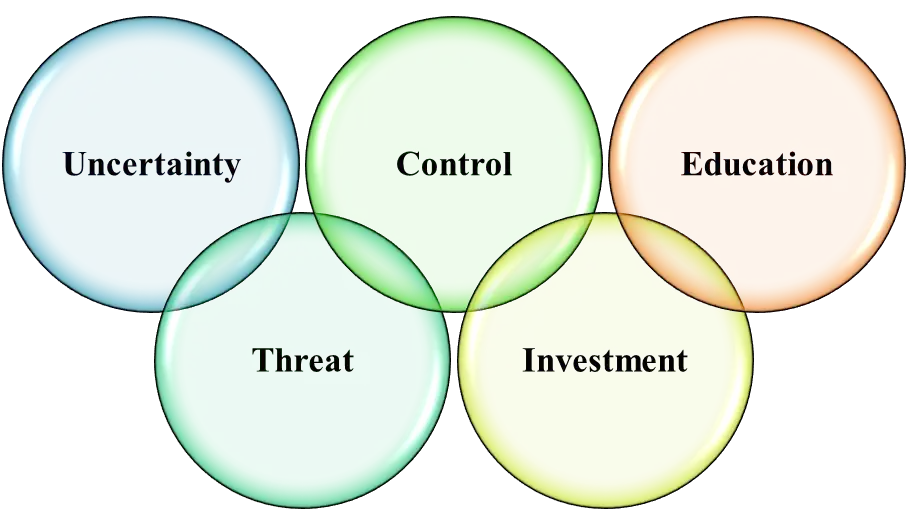
Figure 3: Reason for Adopting Disruptive AR Technology
Uncertainty: The lack of confidence in the AR benefits and skepticism of new processes can mainly impede adoption. The failure of envision change also can restrict engagement and expand the uncertainty as well.
Threat: Disrupting ingrained approaches to working through digitalization creates several threats. Employees mainly perceive AR as threatening professional dependability or skills relevance during their work.
Control: IKEA also inclines toward major control and hierarchical structure. AR solutions mainly require empowering regional experimentation and customer co-creation for resolve this factor.
Investment: Implementing AR mainly demanding the investment of huge time, resources and capital as well. It also convinces stakeholders of return for capital invested may encounter hurdles despite long stretch upside.
Strategies for facing social barriers mainly include:
Education: Immersive AR experiences can quickly build understanding and make belief towards the consumers. Also, the prototypes mainly demonstrate benefits more essentially than concepts.
Ultimately, IKEA needs conviction that AR solutions line up with its identity and values. Active exposure can mainly convert sceptics [Referred to Appendix 2].
The technical Immaturity in Implementation mainly includes:
Displays: The existing smartphone and tablet displays can make projection of realistic virtual objects onto real environments challenging (Ling, et al. 2020). Smart glasses designs can be the main point of evolution.
Processing: Mobile processors today can't deliver the seamless real-time immersive designs and physics simulations required for by far most AR experiences. Cloud upload can help on the latency issues that persist.
Power: Battery technology restricts prolonged active use of processor-intensive in AR applications on mobile devices.
Tracking: AR exactness also depends on precise positioning and mapping of environments as well. GPS, sensors and computer vision capabilities are also able to point prone for errors causing virtual object instability in some circumstances.
These ongoing hardware advances will gradually mitigate the constraints. IKEA can mainly pursue strategies like focused capacity partnerships, moderated rollout and setting reasonable expectations to manage immaturity challenges until the technology evolves further in this fast changing digital world.
Designing complexity is also relevant AR shopping and assembly experiences which requires surmounting some complex design and content challenges:
3D Models: Photorealistic digital models of IKEA's product index with accurate dimensional data are essential for their business (Arzoo, et al. 2021). Current 3D model libraries have gaps which require critical scanning and modeling efforts.
Simulation: Powerful real-time physics engines are needed to impersonate real-world behavior of products in AR. Material, destruction and liquid simulations add complexity for furnishings.
Maintenance: Dynamic indexes and products will necessitate ongoing 3D model updates. Version control and content management systems become fundamental.
IKEA's focus about home furniture’s mainly provides helpful constraints compared to open-ended environments. Progressive building of internal capabilities combined with strategic stage partnerships can mainly overcome complexity over time.
The company’s Customer Adoption Process also identified some difficulties which are as follows:
Hardware: Most consumers actually need AR-capable devices which they not have now. Budget impediments can also restrict purchases.
Proficiency: Interacting in AR mainly requires developing new skills. Digital literacy also varies across IKEA's customer base.
Ergonomics: Prolonged use of headsets can be one of the reason for fatigue. Movement sickness from vestibular frustration is likewise a chance. Ease of use varies by individual, all customers can not gain those ability.
Purpose: Consumers are comfortable with genuine inventories which cannot be seen with AR. Communicating benefits will be essential to build perceived value.
Protection: surreptitiously collecting environment data or biometrics for AR experiences mainly raises security concerns which also ought to be handled transparently.
Strategies to promote customer adoption include:
Multimodal: Maintain genuine records and instructions even as AR capabilities. Give customers a choice in engaging digitally or traditionally for their products.
Incentives: Special offers, cutoff points, and loyalty perks can also motivate initial AR usage.
These factors to experiment with aid learning before targeting mass market adoption (Prassida, and Hsu, 2022). Patience and co-creation will expand AR acceptance over time.
In summary, realizing the potential of AR innovation inside the IKEA firm mainly requires surmounting organizational, technical, and adoption hurdles. None of these barriers are insurmountable. With leadership commitment, investment, and collective ingenuity, the company can gradually integrate AR-centric experiences that add personal and unique dimensions. These vital insights will definitely help IKEA about their brand and business growth in tis digital era of Business.
References
Journals
Key Roles of Operations Management in Ford’s Success Operational management refers to as the process of enhancing the...View and Download
Slide 1: An introduction to Dengue Join thousands of satisfied students who trust Rapid Assignment Help for their academic needs...View and Download
Workplace Transformation And Sales Performance: A Case Study Of Lidl Introduction/Background to the research problem Get free...View and Download
1.0 Introduction Get expert guidance from Affordable Online Assignment Help Experts for top-quality, plagiarism-free work. Enjoy...View and Download
Introduction Experience top-notch Assignment Help crafted by subject-matter experts dedicated to helping you achieve academic...View and Download
Introduction Take a look at this well-organized and thoroughly researched assignment example. It showcases the kind of work our...View and Download
Copyright 2025 @ Rapid Assignment Help Services
offer valid for limited time only*

